Honey Vs Sugar: A Comprehensive Report

Honey Vs Sugar: A Comprehensive Report
Honey is a thick liquid that globally comes in various colours, from translucent whites and golds to amber darker tones. Made by transforming nectar, water, resin, and pollen within the honeycomb into a long-lasting sweet, durable nutrient-rich liquid enjoyed by both bees and humans alike. At room temperature, honey can be liquid, firm, or at some stage between. Another popular sweetener that serves as a focal point of this report is sugar, a diverse range of sweet-tasting soluble carbohydrates. Our human ancestors often struggled to acquire sweet-tasting food outside of their seasonal harvesting periods, which may explain our inability to control ourselves in light of processed sugars and foods.
As a natural sweetener, honey is slowly replacing sugar as the sweetener of choice. This report will explore what these products are? What is the history of both, whilst also exploring how supermarket choices may not provide consumers with the best choices? As honey has a finite supply, certain suppliers have begun adulterating their products with corn syrup to increase profitability. Therefore, corn syrup will be explored briefly.
The report will then move on to examining Honey & Sugar at an industrial scale. What industrial processes must take place for the product to end up on a supermarket shelf? What is the regulation surrounding both products? What byproducts are created during these processes, and ultimately what is the ongoing effect on the global ecosystem? Can the damages made to the ecosystem be reversed? These questions all need to be considered in increasingly an environmentally focused world.
By the end of this report, you would have unpacked several reasons why honeybee numbers are declining. And gained a greater understanding of how processed sugar would need to expand industrial operations to keep up with global demand. You should also be best able to understand the differing natures of raw/supermarket honey.
You can find an FAQ on Honey and Sugar at the end of the report, which answers some popular questions surrounding this topic.
Honey
Honey is recognised as a product made by bees, sweet to the taste and with high nutritional value. Honey, a thick liquid globally, comes in a range of colours. Translucent whites and golds to amber darker tones. Made by transforming nectar, water, resin, and pollen within the honeycomb into a long-lasting sweet, durable nutrient-rich liquid enjoyed by both bees and humans. At room temperature, the product can be liquid, firm, or at some stage. As a natural sweetener, a naturally occurring source of sugar, honey is slowly replacing sugar as a sweetener alternative.
Historically, honey has been human’s sweetener of choice. It was cheaper to obtain than sugar and had a durable shelf life. In the United Kingdom (UK), beeswax was often more expensive than honey itself. It could be used for polishing floors, creating candles and also creating figurines. Madame Tussauds, London’s famous waxwork museum, uses beeswax to make certain parts of their wax figures. Currently, beeswax candles are still more expensive than regular paraffin candles. This is due to them cleaning the air as they burn and because it burns slower than typical candles due to their high burning temperature.
Yet, popular shows such as Rotten: Lawyers vs Honey have shown what is sometimes labelled as honey on supermarket shelves is oftentimes not. This is largely dependent on a country’s legislation. But also the level of diligence a supermarket exerts when verifying the quality of the products on its shelves. The act of honey adulteration has a long history. It can range from mis-sold honey-flavoured sugar syrups to honey that has been bulked with the use of sugars/syrups.
The American Honey Producers Association have banned honey exports from China, meaning the industry leaders have tried to subvert restriction legislation by shipping the produce to neighbouring countries where the pollen is filtered out. Filtering out the pollen means the honey cannot be traced back to its originating source. This pollen-free honey is then sold on to European markets etc.
The Honeybee
There are 8 recognised species of the honeybee with 43 subspecies. The 8 species are Giant Honeybee, the Giant Himalayan honeybee, the Western honeybee, the Asian honeybee, Koschenikov’s honeybee, the Philippine honeybee, the Red Dwarf honeybee, and the Black dwarf honeybee. The honeybee most common in the UK and Europe is the Western Honeybee, otherwise known as Apis Mellifera, Latin for honey bearing. This is the most common honeybee across the globe, one of the first domesticated insects.
Bees are flying insects largely popularised for their role in pollination and the creation of honey. A honeybee will live in a large colony which consists of male drones, sterile female workers, and one Queen. The honeybee plays a special role within the hive yet only makes up a small fraction of the colony. 5 These worker bees typically only live up to 2 months. It is their job to leave the hive searching for pollen, resin, water, and nectar to be brought back and converted into honey within the hive. The job of collecting pollen/nectar is usually split, one bee will collect pollen whilst another will only collect nectar.
While the honeybee is vital to the creation of honey, the bee itself is vital for pollinating numerous plants, vegetables, and crops. A rise in the use of pesticides has put the position of the honeybee in danger. Pesticides are hazardous to bees. It is theorised that bees become poisoned as they fly through areas where pesticide has been sprayed. And if they drink water that is contaminated by pesticides, the bee may get confused on its way back to the hive, potentially regurgitating what it has in its stomach, or worse, situations sudden death. Pesticides also represent a risk for consumers since small quantities often result in the honey produced by the bees.
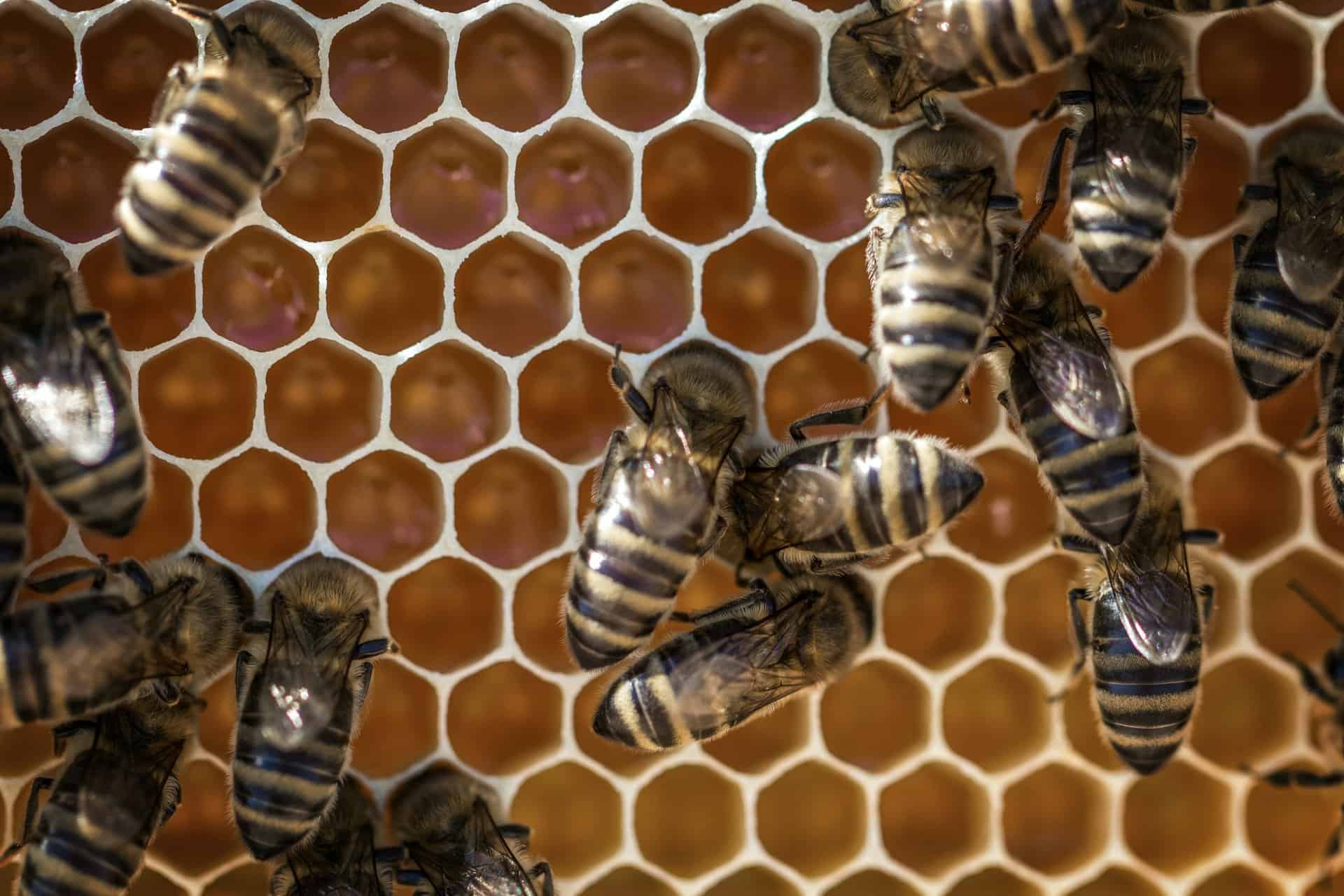
Honeybees use their straw-like tongues to suck up nectar, water, and resin from plants, flowers, and trees they find in the wild. This nectar is then stored in an extra stomach within the bee called a Crip. Inside the bee, the chemical composition of nectar changes; the nectar is enriched with enzymes, proteins, acids, and other substances from the bees. Since the water content is very high in this state, the bee must repeat this process until the nectar droplets are thick and tough enough. Once the water content is balanced, the honey bee distributes the nectar in empty honeycomb cells. By making sure to leave some leeway and not filling the honeycomb to the top, the bee can accelerate the evaporation by constantly fanning its wings, creating sweet, liquid honey.
With a water content of 20% or less, the cell will then be capped over with a thin layer of wax to seal it. When most of the water of the liquid has been evaporated, the bees seal the cob with a secretion of liquid from its abdomen. This secretion hardens to become beeswax. The honey stored within the beeswax acts as a food source for the bees throughout the winter. It can be stored indefinitely. This capping indicates to the beekeeper that the honey is ready to be harvested. Honey is usually harvested during May and August. Bees make honey during the Spring and Summer months. On average, a hive can produce 60 lb or more in a good season. Since honey bees- unlike wasps or humblebees- overwinter as a colony, the Beekeeper has to make sure to leave the hive at least 20-30 lb of honey to survive an average winter. The colony does not hibernate but stays active and clusters together to stay warm. This requires a lot of food (honey) during the cold winter season, and therefore, the remaining honey is essential for the bees to survive. Luckily, a strong colony can produce 3 times more honey than they need.
Honey has historically been enjoyed by many animals including bears, and badgers.
In December 2020, it was found most honey on UK supermarket shelves was, in fact, ‘bulked out with cheap syrups made from rice and corn’. All retailers claim this was done without their knowledge. Whilst investigations are still underway, it seems to be the most current modern-day supermarket food fraud. Honey adulteration has a long history, from sugar syrups with honey flavouring to simply adding sugar and syrups to your honey to bulk the final product. Banned honey exports from China mean the industry has tried to 4 subvert restricting export bans by shipping the product to a neighbouring country where the pollen is filtered out. Giant Chinese retailers such as Alibaba publicly sell syrups for honey adulteration.
The honey market is largely divided into two types: raw honey and pasteurised honey. Raw honey is a mixture of fructose, glucose, water, maltose, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals. Pasteurised honey is usually sold in large quantities. It thereby relies upon buying honey in cheap bulk from countries all over the globe, mixing these bulk purchases, and then selling the final mixture. The pasteurization process kills any active ingredients in the honey preventing fermentation and delaying the onset of crystallization. The mixing together processes increase the consumer's likelihood of consuming pesticides and antibiotics. The genetic makeup of raw honey, when compared to honey syrup mixes, is completely different.
Store-bought pasteurized honey oftentimes has much higher water percentages than honey naturally produced by bees. This is a direct result of beekeepers feeding their bees water mixed with artificial sugars. Pasteurised honey lacks many of the health benefits found in raw honey.
Is raw honey safe? Raw Honey is safe, and it provides many health benefits; nevertheless, it should not be cooked over 40 degrees. When cooked, honey becomes like glue and thus produces toxins. Honey's raw form is the one detaining all its main benefits and properties. By altering its chemical composition by heating or overheating the honey, It may completely change its compounds leading to health hazards. Honey also contains bacteria that can harm a young baby’s intestine. To this end, avoid giving honey to babies under 12 months old.
Honey - A Regulated Product
In the UK, honey is regulated under The Honey (England) Regulations 2015, the devolved powers have their relevant acts. No product is to be labelled honey unless it meets the criteria outlined in the law. This legislation put into law that ‘honey’ means the natural sweet substance produced by bees from the nectar or secretions of plants or the excretions of plant-sucking insects, and stored in honeycombs to ripen and mature.
Blends of honey whether they only from one region of the world e.g. EU member state, or multiple regions of the world, the EU member state and EU non-member state. Are legal, therefore it is even more reason consumers 6 must be wary and vigilant to research and, aim to purchase from transparent businesses.
Considering recent evidence that much of what is contained on the shelves of supermarkets is blended honey syrup mixes. There are calls on the Conservative government to devise a new testing system. The Honey Authenticity Project is an international consortium effort of people and organisations whose fundamental interest is to stop honey fraud (honey fraud or laundering is the adultering of the product), to avoid affecting the rights of producers and consumers, as well as the environment, bees and health.
Honey can come in two forms raw and regular. Regular honey, sold in the supermarket, is pasteurized this, therefore, kills some of the active ingredients within the Honey which make it the most beneficial such as the yeast, it also removes dangerous impurities which may have been there. For the majority of history, humans would have eaten raw honey. Raw honey refers to Honey that exists just as it does in the beehive, and is obtained abstracted settled or strained without adding any heat.
The pasteurisation process also tends to reduce the onset of visible crystallisation.
Sugar
Sugar is the name given to sweet-tasting soluble carbohydrates. As sugars cover a vast array of products, this report will predominately focus on processed sugar or artificial sugar, the product which comes from straining sugar cane and/or sugar beet. Sugar juice must first be extracted for the final sugar product, which we know to be created.
Our ancestors often struggled to acquire sweet-tasting food outside of their seasonal harvesting time and thus relied on fruit. The preference for ripe fruit was due to its high sugar content, which supplied the body with greater energy. Evolutionary biologist Daniel Lieberman put it best 'sugar is a deep ancient craving'. Sugary foods also tend to be fattening food. When food is scarce, or you have to prepare for the impending winter, it could be good to gain weight. Therefore, you could see how communities and populations would come to revere sweet food.
Sugar contains carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms, thereby allowing it to fuel the body. The sugar which comes in supermarkets is often Sucrose. Sucrose is made up of 2 simpler sugars fructose and glucose. In baking recipes, acids such as vinegar or lemon juice break down the sucrose into simpler sugars. When sugar is added to hot water, it dissolves, such as the process in a cup of tea and why the stirring is necessary to aid the dissolving. However, an infinite amount of sugar cannot be dissolved in a cup of tea.
In some regions of the world, such as in the Caucasus', you see that the culture has developed an art of preserving sweetened drinks that preserve fruit for years rather than months, for example, Kompot. But even these sweetened drinks only became widespread once sugar was being traded in Europe. Other fruit preserves also became popular, Jam, Marmalade, and Conserves. These popular foods were first developed in the Middle East but preserving utensils can be found in the Stone Age. These historic humans were most likely preserving not with sugar but honey.
German biologists have argued that the brain's reward system is activated when sugar is consumed, releasing feel-good neurotransmitters. For a small moment post-consumption, you feel good. Fats, drugs, and alcohol also work in similar ways. Over time, individuals thus develop tastes for certain sugary foods. Views conflict as to how addictive sugar is. There are some suggestions, that dopamine a neurotransmitter within the brain which controls mood, behaviour, learning, and, memory can become dependent and addicted to sugar. The evidence is that dopamine receptors become altered over a while due to overconsumption of sugar. This is one reason why people struggle to remove sugar from their diet. Over time, to 8 reaches the initial feel good which came as a result of consuming sugar, more and more sugar is needed.
Sugar - A Breif History
Historically, sugar was quite expensive to produce. The world saw the mass production of granulated sugar with the Trans-Atlantic slave trade. The slave trade aided in making sugar a staple of the British diet across the colony. Until the end of the slave trade, most sugar production was done in the colonies by slaves. Sugar can be described as Khalil Gibran Muhammed described as the white fuel of slavery.
The extraction of sugarcane juice from the sugar cane plant began in South Asia around 4000 BC. This process evolved over a few thousand years as techniques were honed and developed to refine the sugar granule crystals. The domestication of the crop began in Taiwan, Southern China, before moving inland and up into India.
By the 6th century, imperial convoys were sent to India to learn about sugar refinement, notably China. By the late 6th century, Muslims had transported methods learnt to Southern Persia. Once Persia had acquired the methods to refine sugar, each area conquered would also attain this knowledge. The Persians brought Sugar Cane to southern Spain. Around the late 14th century, the sugar press was created. This allowed for more liquid to be released from the Sugar Cane.
Sugar was costly and reserved for the upper class. It was considered in the ranks of spices such as Saffron. This changed when production moved to Latin America and the Caribbean. The 15th and 16th centuries saw Spanish and Portuguese exploration and the transportation of sugar to southern Iberia. The sugarcane is introduced to Madeira in 1425 by Henry the Navigator. On his second voyage to the New World in 1493, Christopher Columbus introduces sugarcane seeds to the Dominican Republic, where the seed did exceptionally well. From there, the seed spread across the Caribbean and the Americas.
By the 16th century, the Portuguese have brought sugarcane to Brazil, developing the foundations for the country to become the modern-day top exporter of sugar. From the early 18th century, Sugar begins to be a major European import as it becomes cheaper. It increasingly becomes a staple of the European diet. It was also around this time that a chemist was able to find sugar in Beet Roots. In 1768, the first steam-powered sugar mill press was created in Jamaica.
At the beginning of the 19th century, Silesia (now modern-day Poland) develops its first sugar beet processing plant. France follows suit, and by the 1830s, plans to bring a sugar beet processing plant to America were underway. Sugar beet had been popular as being a sweet vegetable. Beets reach maturity after 90-95 days, at which point they are harvested. By the 1890s, commercial Sugar Beet plants are commonplace across parts of America.
At this point, the by-products from sugar also begin to develop. Molasses is separated from Sugar, and As technologies develop, you see golden syrup, black treacle, and rum become lucrative by-products. Before the 17th century, the black treacle, one of the sugar production byproducts, was used in medicine. It was then typically used as a meat preservative. But now, we have found a way to consume it mostly whilst baking.
As sugar became cheaper and cheaper, more countries in Europe became addicted to sugar and sugar-derived products, cakes, and drinks. Blackened teeth became a sign of wealth—Europe supplier's workforce. Portuguese colonies had already developed outposts in West Africa to trade Ivory. With too many traders, the extension to selling humans was only an extension of the market system in place. By the middle of the nineteenth century, this market system led to 10 million Africans being forcibly removed. In the three centuries as the system was in place, sugar rose to be Europe's largest commodity.
Brazil, Jamaica, Cuba, and India. As opposition groups, the trade of sugar and slavery, large Garrison were sent to the Caribbean. It could be argued, and loss of America was on to defending its sugar colonies. Ultimately, the trans-Atlantic slave trade ended by the industry for the sugar industry to thrive was in place. Thus you see, today, many of the old sugar colonies are still involved in the trade.
Developments in sugars and sweeteners continued after the end of slavery. In the 19th and 20th-century development, fructose-derived beet sugar of sweeteners, the fruit of corn syrup and increased adulteration of honey. This will be explored in upcoming topics.
Sowing and Processing Sugar Cane
Sugar cane is typically sowed between February and October. Most of the cane harvested comes from Brazil. In 2019, Brazil accounted for 38.61% of the world's sugar cane production. Followed by India. Thailand, China, and the US, Mexico are also top suppliers.
Farmers grow the cane, and they agree with the sugar mill on an appropriate time to deliver the cane. When the sugar arrives at the mill, it’s initially weighted before being prepared for milling via breaking cutting and/or shredding. The juices are then extracted from the mill. The extracted juices are sent to the boiling house for further processing.
The sugar juices are typically treated with milk of lime and sulphur dioxides. This treated liquid is then further heated. The final mix is filtered into liquid and olive cake. The clear liquid is then heated until it reaches a syrupy consistency before being moved into vacuum pans for further concentrating and sugar grain consistency. A thick byproduct is created, which is universally known as either molasses, black treacle, or golden syrup. All three of these byproducts are sold in their own right.
Historically creating cane sugar involves a long, rigorous and, historically dangerous process. The cane must first be crushed to allow for the sugar to be released. The juices collected from the initial crushing will be filtered, potentially chemically treated at this stage, depending on the type of sugar sought. Humans typically had to stir the boiling sugar.
The process for Extracting sugar from Sugar beets is slightly different. Once at the factory, Sugar Beets are first washed and sliced into thin strips. These strips then go into a diffuser where the liquid is extracted. The liquid then goes through a process that removes impurities. Left behind is a syrup. The syrup is dried, and the crystals which are left behind are stored and sold as sugar. The size of the sugar crystal is at the whim of the supplier. Molasses could be introduced to diversify the product range. The product does not have to be bleached.
Raw sugar accounts for roughly 60% of international trade. In places like the USA, sugar is still a highly subsided industry that aims to protect US farmers against low sugar prices from foreign suppliers.
There are a few good uses for Sugar Cane Bagasse. Bagasse refers to the dry fibrous matter left behind from sugar cane after extracting sugar juice. In 1937, the commercial process of turning bagasse to paper was made possible. In some regions of the world, this has been fully incorporated into the sugar cane extracting process. Therefore, a paper plant will be set up next to a sugar refinement factory to convert the unusable by-product into a sailable good. The bagasse is cooked, debris and stones are removed and then bleached to bring it to a bright white colour. Modern paper developments from sugar cane bagasse included postal boxes, envelopes, and tissues.
Paper is not the only material that can be made from sugar cane bagasse. It is also possible for textile materials to be made, which can be used to make clothing.
Then there is the process for bio converting sugar cane bagasse to ethanol. The greatest challenge comes when stabilising ethanol production as a leftover material, as the amount you end up with can easily vary. Some parts of Punjab are said to have already tractors running on this fuel.
Another avenue explored in Kenya is to make Briquettes out of the leftover bagasse and use these as logs for burning instead of wood from trees. Ultimately this converts low-quality biomass into high-quality fuel. This could be a tool to fight deforestation.
The biofuel, which comes from sugar cane bagasse, is eco friendly—the biggest exporter of sugar, Brazil.
Some have been able to use this leftover matter as a building material.
Much Sugar Beet bagasse is used as animal feed, but it can be used for the same purpose as sugar cane bagasse.
Corn Syrup
A Breif History Of Corn Syrup
A cheaper alternative to processed sugar obtained through sugar cane and/or sugar beets is Corn Syrup. It is a sugar-based sweetener, a low-calorie substance used in place of sugar to sweeten food and drink. High fructose corn syrup (HFCS) was first created by Richard O. Marshall and Earl R. Kooi in 1957. In Europe, it also goes by the name fructose glucose syrup or glucose-fructose syrup.
HFCS is made when the enzyme composition is rearranged, changing glucose into fructose typically. It was produced from corn that would be milled down into corn starch, otherwise known as cornflour in other regions of the world, this starch will then be changed into corn syrup. To finalise the process, you would add glucose isomerase enzymes. Initially, HFCS wasn't very popular. Carbonated drinks suppliers such as Pepsi and Coca-Cola switched from using sugar to HFCS in the 80s to cut production costs. Today, you can see that in many packaged foods, HFCS has replaced the traditionally utilised cane sugar. In a similar manner to which cane sugar replaced honey. In comparison to Sugar common, HFCS is cheaper to manufacture and easier to transport. You also do not need much corn to create the syrup making it agriculturally feasible.
Fructose never used to be such a part of the human diet. It is only in the last century that we see widespread consumption, increase due not only to the availability of HFCS but also its uptake by large companies. You find fructose in sugar cane, sugar beet, honey, and HFCS. Research does point towards evidence that high fructose consumption can lead to deleterious metabolic effects. These syndromes include high blood pressure, high blood sugar levels, and a likelihood to become obese.
The commercial production of HFCS. In Europe, the EU previously capped production by a quota. HFCS, therefore, isn't as prevalent in food as it is in America only because there isn't enough HFCS in production to ensure a product company can access HFCS in the future.
Proponents arguing against the use of HFCS argue that when it is used to sweeten food, it becomes difficult to regulate the amount of sugar entering the body. This thereby contributes to not only obesity but also sugar addictions. One Princeton University study showed that when rats had access to HFCS and normal table sugar full stop, those who consumed HFCS over a long period experience abnormal increases in weight gain, especially around the abdominal area and 13 blood fat being circulated throughout the body.
Globally, China makes up for most of the global demand whilst also selling it cheaply. There were once pushes to have HFCS renamed as corn sugar, but these did not amount to any change.
From 2004, schools, especially in the US, began pushing to stop having soda sold especially due to what they deemed the effects of HFCS. The research surrounding HFCS varies. In 2005, researcher Alan Gaby believed HFCS was exacerbating the ageing process. As one of the key contributors to diarrhoea.

Honey & The Human Body
This section will focus on the impact of honey consumption on the human body. To begin, we differentiate between two different types of honey; Raw/store-bought or processed honey. Raw honey is a mixture of fructose, glucose, water, maltose, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals. Cheap honey relies upon buying honey in cheap bulk from countries all over the globe, mixing them, thereby increasing the consumer's likelihood of consuming pesticides and antibiotics. The genetic makeup of raw honey, when compared to honey syrup mixes, is completely different. Raw honey, whilst containing impurities, will also contain active ingredients which oftentimes have antibacterial properties, making them efficient in killing unwanted germs.
Glucose Oxidase is one such enzyme that contributes to honey’s antibacterial properties. Within honey, glucose oxidase catalyses the oxidation of glucose to hydrogen peroxide. It is then it begins to act as a natural preservative. Therefore, active raw honey with glucose oxidase present when applied to a wound could aid healing. Glucose Oxidase, whilst present in honey is also being used to aid home blood monitoring devices for diabetes management. Therefore, the consumption of glucose oxidase is beneficial to humans. But in other areas, glucose oxidase is being tested to try and increase the shelf life of food. Being developed for uses in food colouring and even improving the texture of food products.
In 2016, Nigeria a research team began researching the immune-modulatory properties of raw acacia honey. There believe within the honey, there are bioactive compounds that could potentially be used for cancer treatment and potential prevention. This is not the first study that highlights the ability of raw honey to aid in illness prevention. You need to be careful of Botulism, toxins caused by Closterium botulinum bacteria, some of the most aggressive toxins known to science that can sometimes be present in raw honey. Whilst it is scarce to contract, the onset of illness can still be life-threatening. It can lead to muscle paralysis by attacking the nervous system. This paralysis is not halted can spread to the lungs, making it impossible to breathe. Warning signs include difficulty breathing, diarrhoea, vomiting, blurred vision, and weakness. It should be noted botulism has been found in ham, sausages, and tinned food. In the absence of oxygen, these spores germinate, grow and excrete toxins.
Store-bought cheap honey oftentimes has much higher water percentages than honey naturally produced by bees. This is a direct result of beekeepers feeding their bees water mixed with artificial sugars. Individual gardeners have also been encouraged in some regions to leave tubs of sugar water in 15 gardens for bees to sip. This may be exacerbating the issue. Another problem with store-bought honey is its lack of pollen. Local honey is only best used to alleviate hay fever symptoms if it includes pollen. In this way, the honey can act similarly to an allergy shot, immunotherapy whereby you trigger your allergy via small consumption or injection of your allergen. Overtime consumption may be able to increase, and symptoms may be alleviated.
The health benefits of honey will therefore vary depending on which kind you buy. Raw honey, in this case, is the best option. When consuming honey, you should also seek honey from areas that have been uncontaminated and where the bees have not been treated with antibiotics. In 2017, nearly 79% of European honey, when part of a randomised study, contained potent pesticides. In 2018, a quarter of honey on the shelves showed to be contaminated by bee-harming pesticides, so this is a UK and Europe-wide problem.
Is raw honey safe? Raw Honey is safe, and it provides many health benefits; nevertheless, it should not be cooked raw over 40 degrees. When cooked, honey becomes similar to glue and thus produces toxins. Honey's raw form is the one detaining all its main benefits and properties. By altering its chemical composition by heating or overheating the honey, It may completely change its compounds leading to health hazards. Honey also contains bacteria that can harm a young baby’s intestine. To this end, avoid giving honey to babies under 12 months old.
Honey is a healthier alternative to sugar, it sweetens similarly yet is safer for the body, especially for those affected by diabetes or glycaemia. Raw honey especially contains antioxidants that help reduce the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and some types of cancer. It lowers blood pressure and improves cholesterol values. Honey is great for healing wounds and burns. Several micronutrients are prevalent in honey, such as potassium, iron, and zinc, beneficial to the human body.
The marketing of honey can be an interesting topic, it is often marketed as a healthier alternative to Sugar. Some dismiss honey as too high in sugar and look down upon its caloric values full stop, which is often higher than low-calorie sweeteners.
Honey On Human Skin
High-quality honey contains phenolic acids and flavonoids (otherwise known as antioxidants), which help fight disease-causing cells. Directly applying honey to wounds can also aid in the healing process, reducing scaring and keeping wounds clean. The antibacterial properties of honey can decrease the growth of bacteria, which can lead to infection. Similar results were found when humans applied honey 16 to wounds on the feet, such as ulcers.
Evidence is currently unclear, but potentially, honey can also be used for skin conditions ranging from dermatitis to eczema. The moisture could aid in speeding up healing.

Sugar has developed quite a bad reputation, not only due to its contributing effects to the ongoing global obesity crisis. But also, simple sugars especially have been pushed as empty calories. Therefore, sugar-laden foods and drinks are ultimately low-nutrient foods. Think of sweets, fizzy drinks, and French fries. Whilst all carbohydrates can be absorbed and used by the body, the body better uses protein and vitamins rather than pure carbohydrates. This is one reason health organisations have tried to push limitations on daily sugar consumption. Human dietary needs are better met when they consider the nutrient density within the sugary foods they consume.
When sugar is consumed, the enzymes are broken down in the small intestine into glucose. When glucose is transported to tissue cells, it then travels onward to muscles and organs, where it is then converted to energy. Beta cells in the pancreas monitor the amount of glucose in the bloodstream. Any glucose which goes unused within the day is then converted into fat. An overconsumption of sugar leads to high levels of insulin which in turn affects the arteries. The arteries harden over time and become increasingly resistant to insulin.
Over time, with too much sugar consumption, you increase your susceptibility to illness, including heart failure, obesity, and a range of other illnesses. Within the brain, you may become susceptible to cognitive deficiencies. The mouth can experience tooth decay and cavities. If there is too much sugar in your body, it may resist insulin resulting in Diabetes.
A slow but gradual increase in the consumption of processed, packaged, and fast foods. A high in sugar has led to many humans consuming more than the recommended sugar allowance. This is the same with sandwiches and other products. Global predictions still believe the confectionery and beverages markets are still set to grow.
One study which compared 30-day usage of table sugar to 30-day usage of Honey in 55 individuals found those who consumed honey had their bad LDL cholesterol decreased whilst the good cholesterol HDL increased. Within animals, a similar result was found. Animals who consumed honey will be less likely to have high blood pressure. You must consider that Sugar does not necessarily have much nutritional value whilst honey contains many vitamins and nutrients. It can therefore be metabolised within the body better.
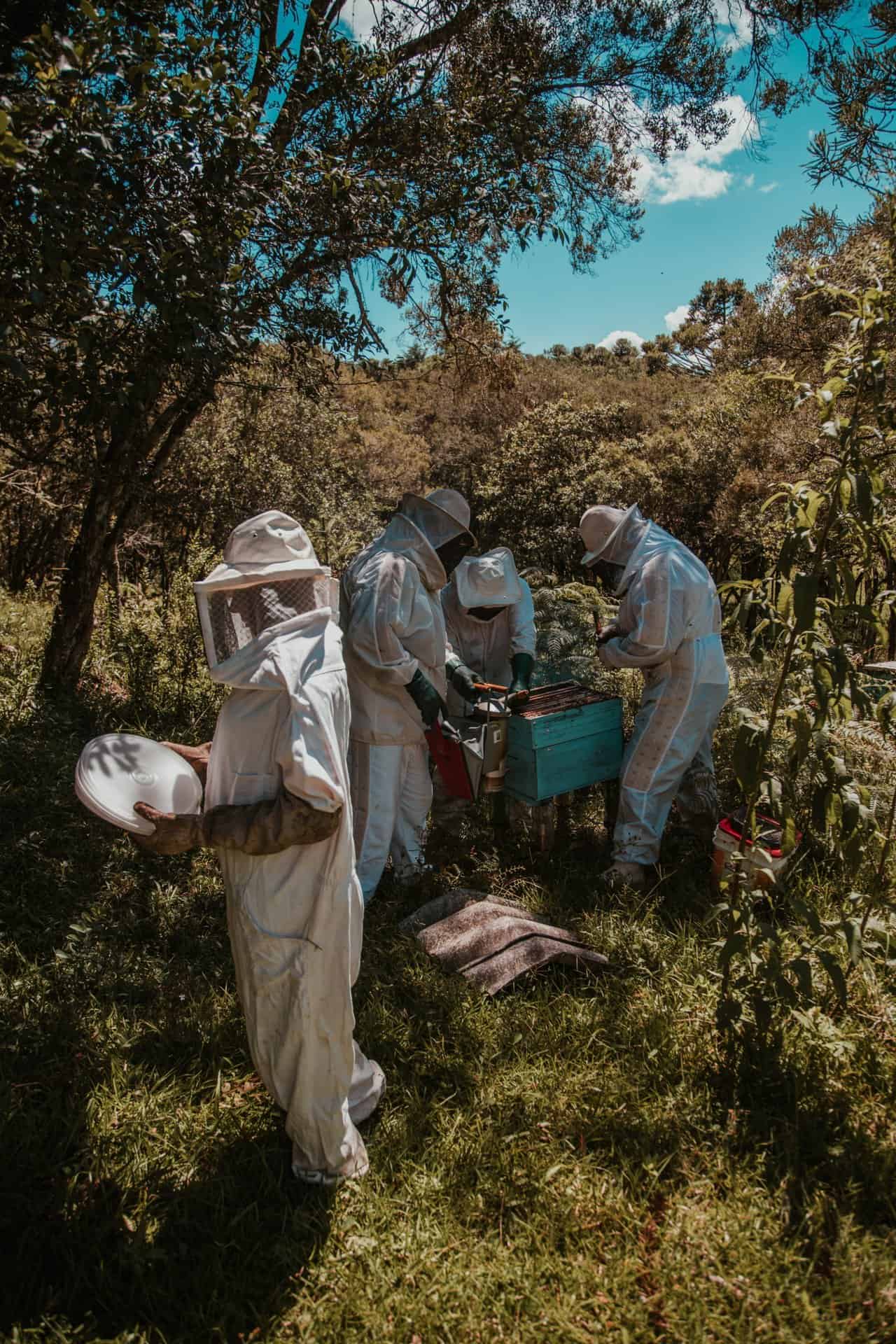
The industrial process of beekeeping is nothing new. It is believed beekeeping was prevalent in Ancient Egypt 5,000 years ago. Apiculture is the practice of keeping and maintaining bees and their hives. The beekeeper is also referred to as the apiarist, and the entire colony set up is called the Apiary. Most beekeepers are still hobbyists, but the honey acquired through a Supermarket is more likely to have been acquired through a commercial beekeeping operation.
Commercial beekeeping is much different to a historical, modern, or hobbyist Apiary. Commercial beekeeping is a large operation. Typically growing to keep up with supply. As honey adulteration has a long history, the profitability of beekeeping operations is increasingly waning. Honest commercial beekeepers cannot keep up with syrup adulterated operations. In 1933, Adam and Todd explored this issue and confidently found that a beekeeper makes $0.045 per pound of honey.
What can often be forgotten is the price of building an adequate hive, purchasing bees, protective wear, machinery, upkeep, and ultimately disease/pest prevention. All of which will contribute to the final amount, if any, honey.
Another part of commercial beekeeping is the pollinator on-demand service.

The global sugar industry has been found to have a devastating effect on soil, air, water, and local populations. This industry is reliant upon the sugar derivatives extracted from cane and beet. The sugar from this industrial process is sold granulated, pure or refined, but it also becomes the main ingredient of beverage drinks, baked goods, candy etc. The sugar industry paid off-market officials to hide the effects on biodiversity.
One of the main environmental issues associated with sugar production is the clearing of natural forests. This is still taking place in Brazil’s Atlantic Forest but was also a problem in Bolivia. The area is cleared or razed for the planting of sugar cane. Empresa Azucarera San Buenaventura (EASBA) is one company that has been called out for its deforestation methods. They combat environmentalists by saying sugar cane infrastructure is needed to bring extra profits to the country. A brief look into their investment plays highlights that they expect more land will be needed for continued development into 2023.
EASBA run the risk of making Bolivia dependent on sugar exports as can be seen from ex-sugar colonies such as Jamaica which rely upon the trade today.
Another issue with sugar cane especially is that the soil can degrade quickly. Sugar cane is often grown best on land where cane has never been grown before. This can mean farmers are constantly in search of new land. Long-term sugar cane farming leads to a decline in soil organic matter. The same goes for Sugar beets, with soil loss from each harvest.
Water sources have to be diverted as sugar cane is usually a water-intensive crop.
The by-products of Sugar cane production also pollute rivers. Some of the worst modern-day damage can be seen in part of Brazil. Some companies still dump wastewater into the rivers.
Across Latin America, there have also been reports of an illness that spreads across sugar cane plantations. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is well documented to be killing men who work on sugar cane plantations. Potentially, the blood sugar levels reach too high a level for the kidneys to adequately clean the system.

"2,196,035 Total acres of sugarcane are certified through Bonsucro, a rigorous certification program founded by WWF that addresses both human needs and environmental health. Honduran sugar mill Azunosa recently received certification as the first Bonsucro member in Central America."
Honey - Impact On Ecosystems
Supporting supermarket honey may not be the best thing for bees. As vital pollinators, bees have a major role in pollinating many crops that humans rely on. For the last few decades, a decline in bee numbers has been noted. The livelihood of bees is therefore of importance to humans. If you see a bee potentially pollinating or a swarm of bees searching for a new home, this is a sign of a healthy environment. Currently, the UK is trailing behind other countries in Europe as they have stabilized their honeybee declining numbers since 2010.
In Europe alone, 80% of the wildflowers are pollinated by bees keeping the countryside picturesque and beautiful. But Bees have less habitat to roam than they once did. With 20,000 species searching for space in an ever small countryside It is challenging for the honeybee to find enough space to roam and food to consume to support a colony. A honeybee's natural habitat would be a shaded forest area where it would home in the bark or the roots.

Loss of Pollinator Habitats
Across the UK, there is widespread loss of pollinating insects. Researchers are increasingly suggesting that there has been a decline or deterioration in UK's biodiversity diversity and non-crop pollination services. Bees have lost a lot of their once pollinating areas habitats to not only agriculture, and Farmland, but camping sites, parks, and residential areas. Every time land is developed, the natural population is displaced in these circumstances that can be wildlife if and microsystems.
However, green space which is simply left to grow on its own accord is also a problem. Habitat quality is important for bees. Thus, they cannot find what they need in an unkempt wasteland.
Cities and urban areas will naturally see the degradation of certain populations of beer as some like to nest in the ground. As this ground is trampled underfoot it makes it too difficult for the Bee to survive in this environment therefore they naturally leave or die out.
Habitat Fragmentation
When an area is broken apart into smaller areas, this too can be difficult for the Bee to navigate. Road construction, for example, was split an area into two. The new habitat created for the Bee may not be large enough to support the entire colonies dietary needs. The pollution from dust and cars could also affect how the bees behave, potentially causing them to find a new hive.
Monoculture
Giant industrial, agricultural operations that maximize profits have created large bands of acres in kilometres, making it difficult for pollinators to find adequate nutrition. US Almond growers, for example, regularly have to bring in suppliers to pollinate all of their trees. This is as there are not enough bees in the world to pollinate these farms or agricultural operations.
Loss of Wildflowers
Europe in particular is one region of the world that has experienced a loss in wildflowers. The eradication of British meadows has led some to call for government actions, some small community groups are also trying to rewild the countryside. This now means some flower species and even fruits such as wild strawberries are on the decline.
Changes in agricultural practices have also influenced the life of honeybees. The 21st century saw the big take off with pesticides and herbicides, with the first decade seeing a steady increase year on year. A rise in the use of pesticides has put the position of the honeybee in danger. Pesticides are hazardous to bees. It is theorised that bees become poisoned as they fly through areas where pesticide has been sprayed. And if they drink water that is contaminated by pesticides.
Pesticides may make a bee regurgitate what it has in its stomach, thereby reducing the food brought back to the hive.
In the worst cases, pesticides and herbicides can lead to many bees dying, including the Queen. This may be noted via a large number of dead bees visibly seen outside of a hive.
The Spread Of Disease
Like all other insects, Bee’s are susceptible to parasites and viruses. Most of these are spread during the movement of Bees, but can also be acquired through contaminated equipment. This next section will take you through several viruses and infestations which commonly affect honey bees.
Acarapiosis is caused by a mite that feeds on the Bee’s hemolymph, the fluid equivalent to blood in most invertebrates. When these mites infest a hive in a large number, there is a high level of mortality.
There are two types of Foulbrood, American and European. American Foulbrood (AFB) is a disease caused by bacteria that kills the larvae within the cell. This bacteria is so resistant it is often the best cause to burn the hive and all equipment, European Foulbrood (EFB).
Bees & Antibiotics
Following on from the point above, Antibiotics are increasingly being used to try and halt diseases that are spreading through colonies. Some of these antibiotics make bees weak and lethargic leading to less productivity.
Colony Collapse Disorder
Colony Collapse Disorder is a term coined to describe the disappearance or death of an entire colony. In some circumstances the whole colony will leave, leaving only the Queen behind.
Colony Death
In the worst scenarios, the whole colony simply dies. A hive may die for many reasons. It may be infested by drones (male bees). It could be due to natural reasons such as a cold spring, sudden frost. Or, starvation, there may not have been enough flowers and pollen available to feed the hive.
These are just some of the many reasons why honey and other types of bees are less prevalent in the wild than they were once before.
Sugar - Impact On Ecosystems
Sugarcane is one of the most water-thirsty plants in the world. A member of the grass family, Sugar cane grows 2-6 metres tall. For most of the Year, the sugarcane sits in water-heavy soil. The World Wildlife organisation estimate that 9 gallons of water are in 2 about 1 tsp of sugar. This often means other ecosystems suffer as a result of Sugar Cane farming.
The rush of farmers moving into the sugar industry has also created or exacerbated deforestation in certain world regions. Brazils Atlantic Forest has notably been affected. To meet global sugar demand by 20-50%, more land will need to be razed so sugar cane plantations can either expand or be established. This would only put more pressure on wildlife populations in Latin America who rely upon the rainforest habitat. In Uganda, rare species of animals were moved to make space for plantations. Within 5 years (2000-2006), 25% of the forest floor was removed, disrupting large concentrations of biodiversity. It is likely the same thing is already underway in Latin America.
If you examine a country such as Jamaica, you see the true impacts on biodiversity can be great. Countries reliant upon sugarcane and cane/beet derived products can use up to 50% of their land to grow the crop.
Is Honey better than Sugar?
- Honey has a lower glycemic index than sugar, meaning it is less likely to cause a spike in blood sugar levels. This can be beneficial for people with diabetes or other blood sugar-related conditions.
- Honey contains antioxidants and enzymes that can be beneficial for overall health, such as reducing inflammation, improving heart health, and boosting the immune system.
- Honey has a unique flavor profile that can be used to enhance the taste of various foods and drinks. It can be used as a sweetener in cooking and baking, and it can also be used in marinades and dressings.
- Honey is a natural sweetener, while sugar is a processed sweetener. This means that honey is not stripped of any of its natural nutrients during production, while sugar is.
- Honey is a natural product produced by bees, while sugar is a processed product that requires large amounts of land, water, and pesticides to produce. This means that honey production has a much lower environmental impact than sugar production.
- Honey has been used for medicinal purposes for thousands of years, and has been found to have antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Honey has been found to be effective in treating coughs and sore throats, and can be a healthier alternative to cough syrups.
- Honey has been found to be effective in promoting wound healing and reducing scarring.
Please note that honey is a sugar and should be consumed in moderation. Additionally, it is important to note that the benefits of honey may vary depending on the type of honey, as well as how it is processed, stored and packaged.
The yearly depletion in processed sugar sales highlights the global move away from processed sugar and a search for alternatives. Many have found that alternative to be honey. It made sense for humans to go back to a long human history with what they’re familiar with. However, now that global trade has emerged which sees the viability of honey is put into question. It is more important to ensure the product you’re consuming is raw and locally sourced. Whilst it can be easy to opt for a bag of sugar, there are many inherent benefits to honey. When you compare the impacts on the environment, it becomes clear that honey is the more sustainable option.
Deforestation sets to off-balance the world even more, especially in this ongoing battle against climate change. Purely to deforest for more sugar cane space, yet honey production relies on no deforestation.
Sugar cane processing factories have been damaging environments for 100’s of years, and they intend to continue to do so. To continue to meet global demand, companies are still planning deforestation. Beekeeping, on the other hand, even at the commercial level, has less of an impact on society. That being said, the future of honey bees is potentially in future, highlighting more may need to be done in the UK to ensure their stability.
When choosing honey products, Supermarket honey has long been identified as a good route for questionable suppliers to get adulterated products on the shelf. It seems wisest to opt for raw, locally-produced honey to get the best health benefits.
FAQs About Honey Vs Sugar
Consuming honey rather than sugar has obvious advantages. The supply to the body of energy in the form of glucose and fructose, simple sugars that do not require any digestive process. Honey also contains Vitamins and other useful enzymes.
Made through the transformation of nectar, water, resin, and pollen within the honeycomb into a long-lasting sweet durable nutrient-rich liquid enjoyed by both bees and humans alike.
Sugar is the name given to sweet-tasting soluble carbohydrates. Processed sugar, the product which comes from straining sugar cane and/or sugar beet. For the final sugar product which we know to be created, sugar juice must first be extracted
Corn Syrup also goes by the name fructose glucose syrup or glucose-fructose syrup. It is a sugar-based sweetener, a low-calorie substance that is used in place of sugar to sweeten food and drink.
Raw Honey is safe and it provides many health benefits, nevertheless, it should not be cooked raw over 40 degrees. When cooked, honey becomes similar to glue and thus produces toxins. Honey's raw form is the one detaining all its main benefits and properties. By altering its chemical composition by heating or overheating the honey It may completely change its compounds leading to health hazards. Honey also contains bacteria that can harm a young baby’s intestine. To this end avoid giving honey to babies under 12 months old.
Raw Honey is a product with many calories; approximately 320 kcal for 100g. Moderation is the key if one has a particular diet. The positive fact about honey is its sweetness. One teaspoon of honey weighs about 7gand it's more than enough to sweeten your favourite cup of tea.
Honey is a healthier alternative to sugar, especially for diabetics. It has antioxidants that help reduce the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and some types of cancer. It lowers blood pressure and improves cholesterol values. Honey is great for healing wounds and burns.
Honey is a great solution for coughs both for children and adults.
We know you're buzzy; but it's so easy to sweeten someone's day!
1 thought on “Honey Vs Sugar: A Comprehensive Report”
Comments are closed.












Very well said! Thank you for sharing this detailed article about honey. Indeed, honeys have a lot of benefits, especially to our health. That’s why I really love having one in my home.