Flowers and Bees
Flowers and bees have a unique and critical relationship in the natural world. Flowers provide a source of food for bees, and in turn, bees are essential pollinators for the reproduction and survival of many flowering plants. This interdependence between flora and fauna has been a subject of study for centuries, with numerous research efforts aimed at understanding the role of bees in pollination and the effects of various environmental factors on their populations.

This article will review the current state of knowledge regarding the interdependence between flowers and bees. We will explore the different types of flowers that are important sources of food for bees, and how these flowers attract and support other bee species. We will also examine the role of bees as pollinators, including pollination mechanisms, the types of flowers they visit, and the factors that influence their behaviour.
“The bee is more honored than other animals, not because she labors, but because she labors for others.”
Saint John Chrysostom
The Interdependence of Flowers and Bees
The relationship between flowers and bees is complex and mutualistic, with both relying on each other for survival and reproduction. Flowers need bees to transfer pollen from male to female reproductive parts, allowing for fertilization and the creation of seeds. In turn, bees rely on flowers for food and energy.
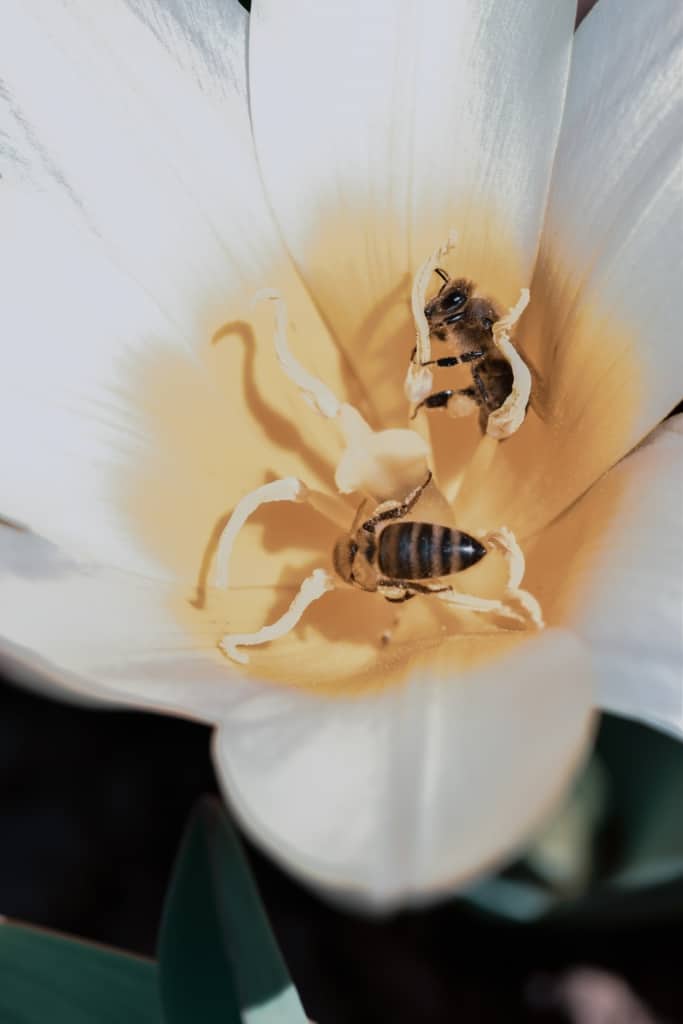

One important aspect of this relationship is the fact that many flowers have evolved to specifically attract bees through visual cues, such as colour and pattern, and olfactory cues, such as scent. These cues not only attract bees but also provide information about the flower’s reproductive status and the availability of nectar and pollen. For example, some flowers have evolved ultraviolet patterns that are visible to bees but not to humans, to guide them to the reproductive parts of the flower.
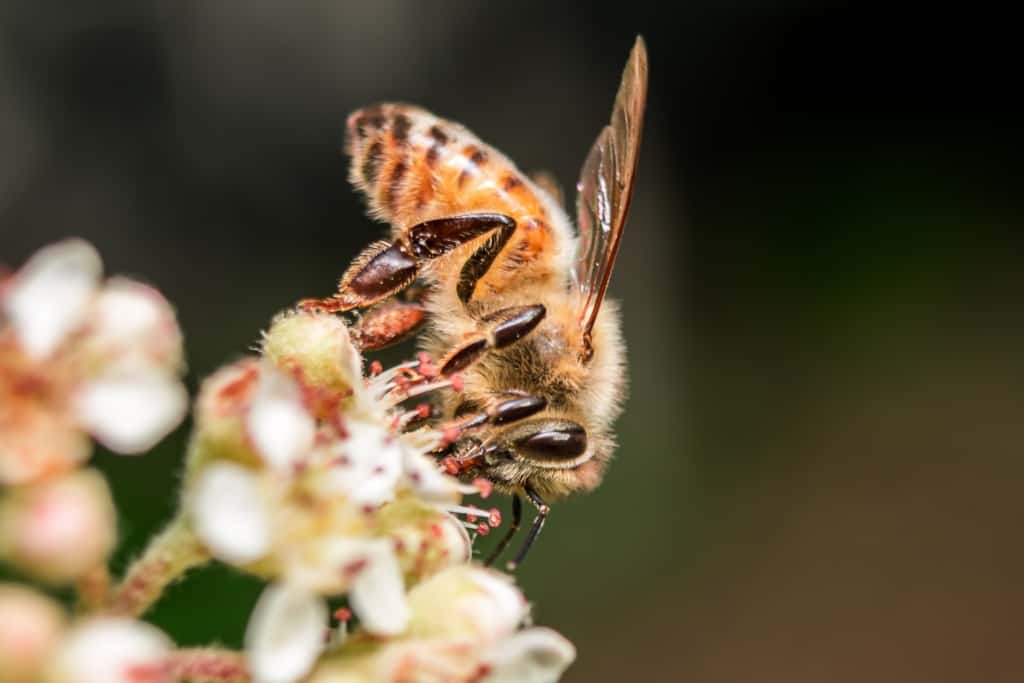

In addition, the timing of flowering and the availability of food sources for bees are crucial to the survival of both flowers and bees. For example, in temperate climates, the timing of flowering is critical, as it ensures that bees have enough food to build up their energy stores in preparation for winter. If flowers bloom too early or too late, there may not be enough bees to transfer pollen and ensure the survival of the plant species.
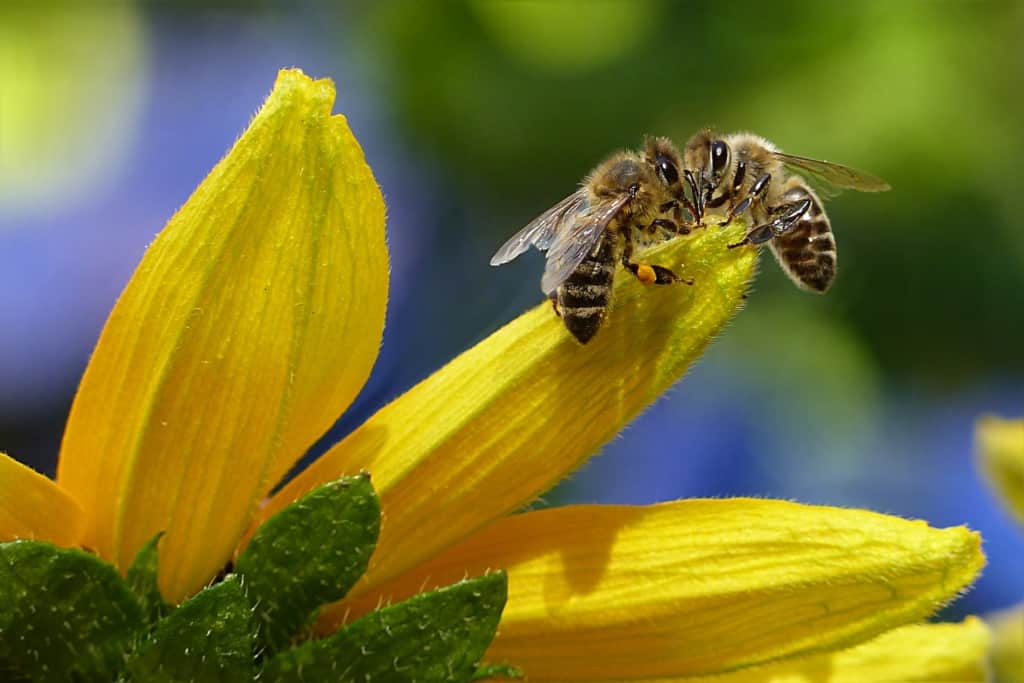

However, the relationship between flowers and bees is not always positive. The use of pesticides, loss of habitat, and climate change have all had negative impacts on bee populations, which in turn affects the pollination and reproduction of flowers. For example, the widespread use of neonicotinoid pesticides has been linked to declines in bee populations, and has been shown to impair bees abilities to find and collect food, navigate, and reproduce.
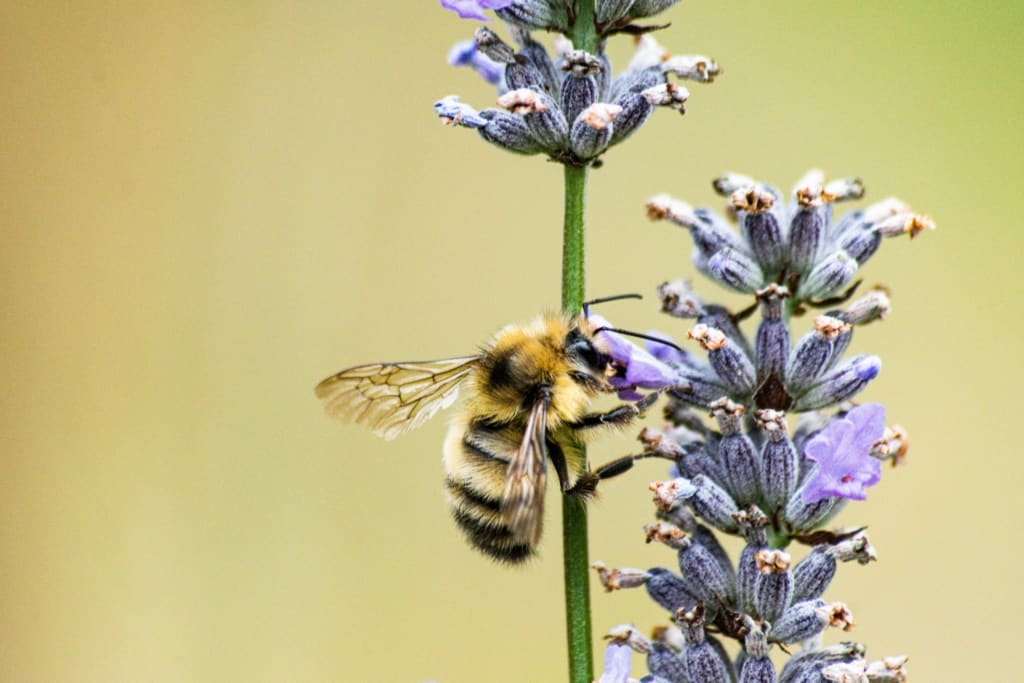

Therefore, it is important to understand the interdependence of flowers and bees and to take steps to protect and conserve both. This can include reducing the use of pesticides, preserving and restoring habitats, and creating habitat corridors to connect fragmented landscapes. Additionally, planting a diverse range of flowering plants can help to ensure that bees have access to a variety of food sources, and can provide habitat for other pollinators such as butterflies, moths, and hummingbirds.
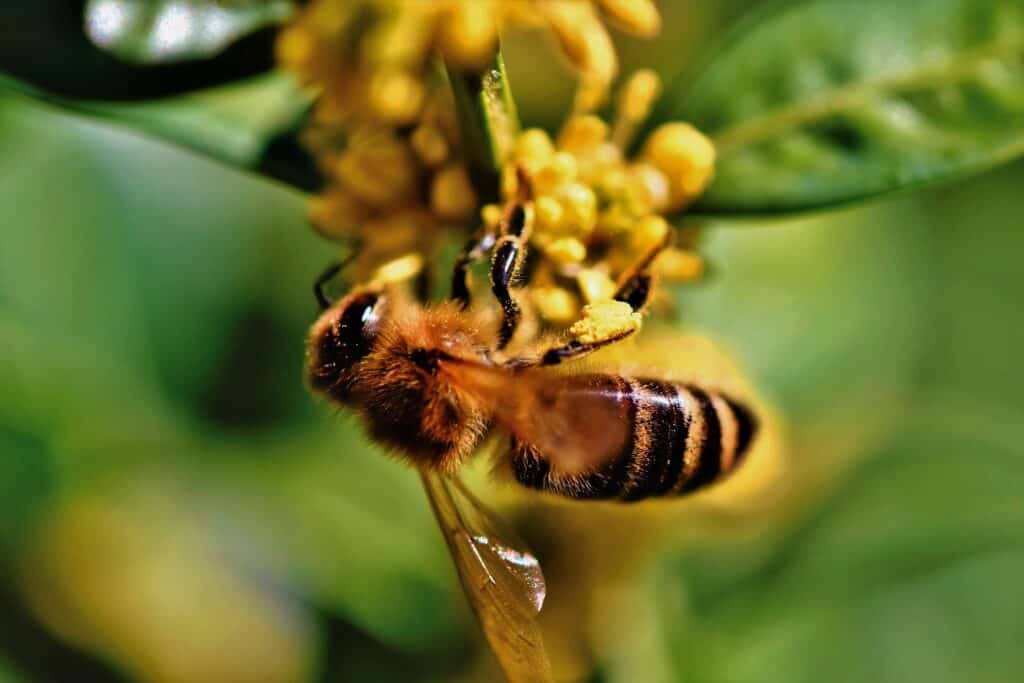

The relationship between flowers and bees is essential for the survival of both, and highlights the importance of understanding and protecting the relationships between species in ecosystems. Further research is needed to fully understand the interdependence of flowers and bees, and to develop effective strategies for conservation and management.
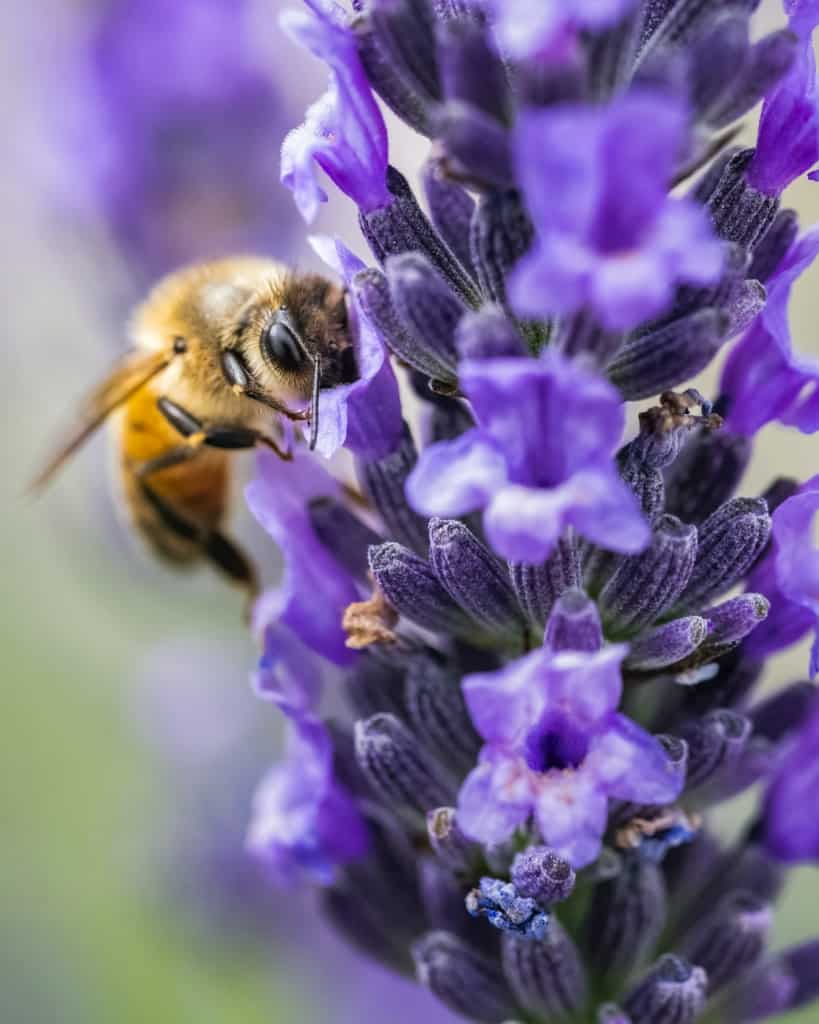

Flowers play a critical role in the ecological system, as they provide essential resources to various organisms, including insects, birds, and small mammals. Flowers serve as a source of nectar and pollen, which are essential components of the diet of many insects, including bees. Nectar is a sugary liquid that provides energy to insects, while pollen provides them with proteins and other essential nutrients. Flowers also serve as a vital source of food for many bird species, which feed on insects, nectar, and fruits.
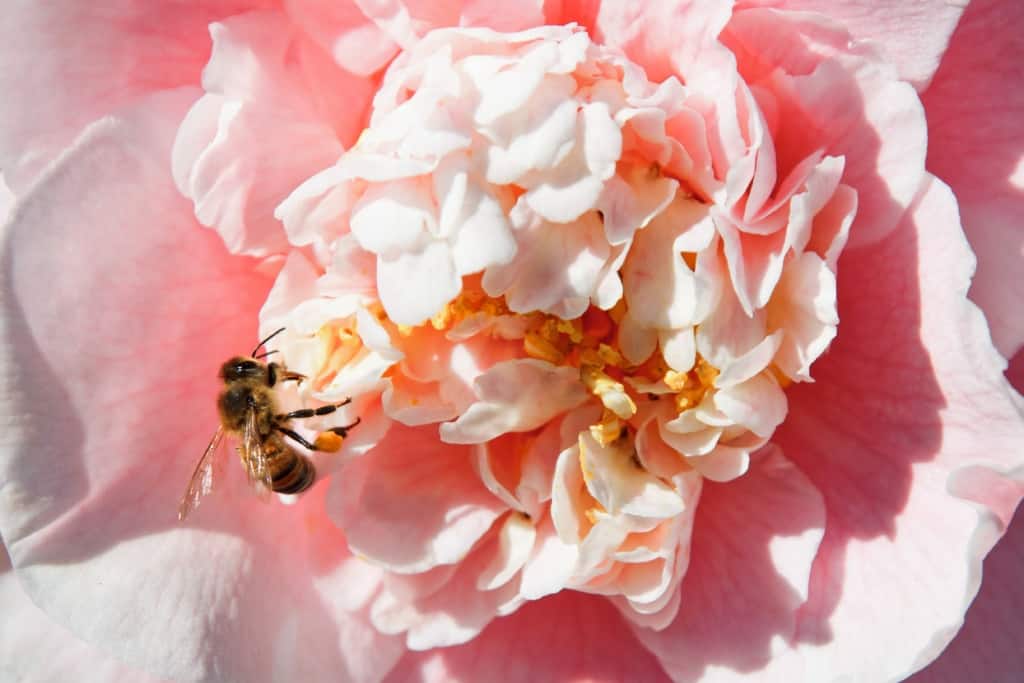

Flowers are also an essential part of the reproductive system of plants. They contain reproductive organs that produce seeds, which are necessary for the growth and survival of plants. Flowers are responsible for attracting pollinators, such as bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds, which play a critical role in the pollination process. Pollinators transfer pollen from one plant to another, allowing for cross-pollination and the production of fertilized seeds. Without pollinators, many plant species would be unable to reproduce and would eventually become extinct.
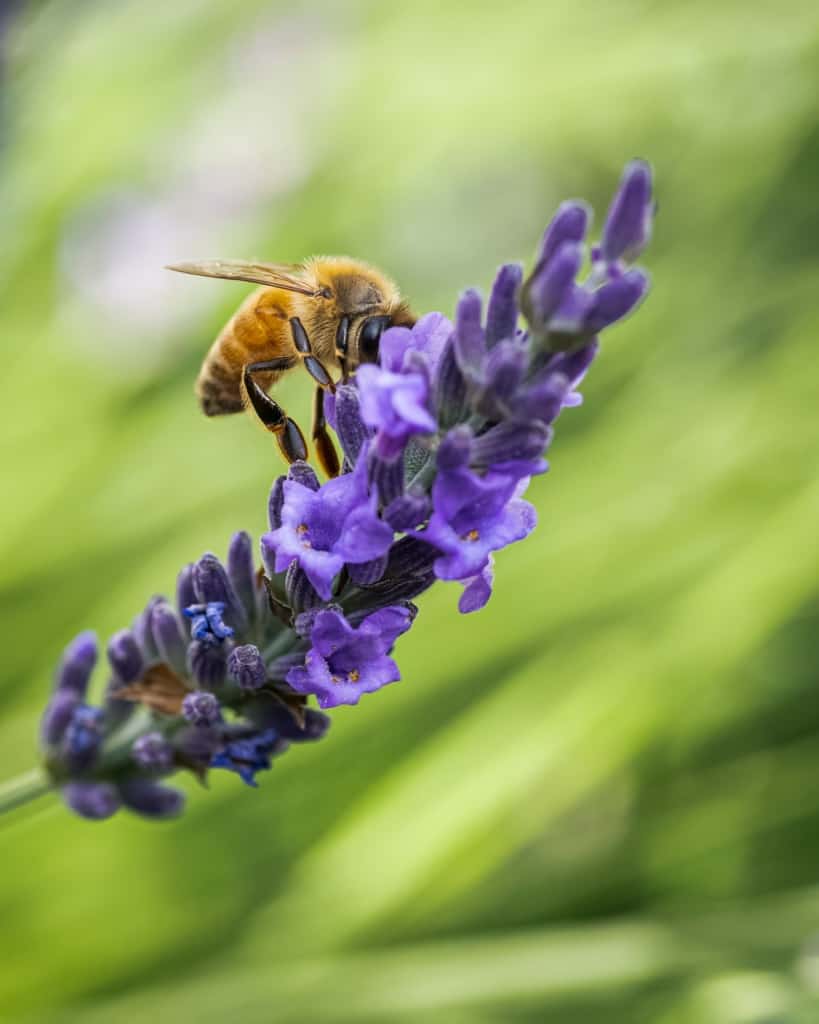

The presence of flowers and their interactions with pollinators also contribute to the maintenance of biodiversity in ecosystems. Flowers come in a variety of colours, shapes, and sizes, and their diversity helps to attract a wide range of pollinators, which in turn helps to ensure the genetic diversity of plants. Flowers and pollinators also play a role in maintaining the structure and stability of ecosystems, as they help to control the populations of herbivores, parasites, and predators.
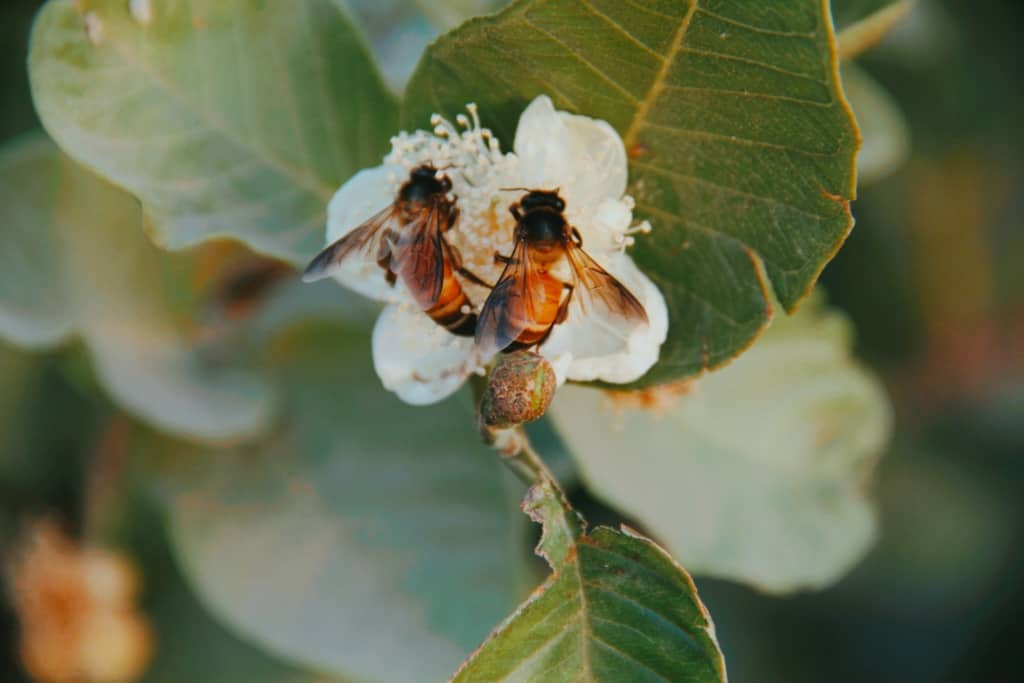

In conclusion, flowers are an essential component of the ecological system, as they provide essential resources to various organisms, including insects, birds, and small mammals. Flowers also play a critical role in the reproductive process of plants and the maintenance of biodiversity in ecosystems. Without flowers, many species of plants, insects, and birds would face extinction, which would have significant implications for the overall health and stability of ecosystems.
The Role of Flowers in the Ecological System
Flowers play a critical role in the ecological system, as they provide essential resources to various organisms, including insects, birds, and small mammals. Flowers serve as a source of nectar and pollen, which are essential components of the diet of many insects, including bees. Nectar is a sugary liquid that provides energy to insects, while pollen provides them with proteins and other essential nutrients. Flowers also serve as a vital source of food for many bird species, which feed on insects, nectar, and fruits.
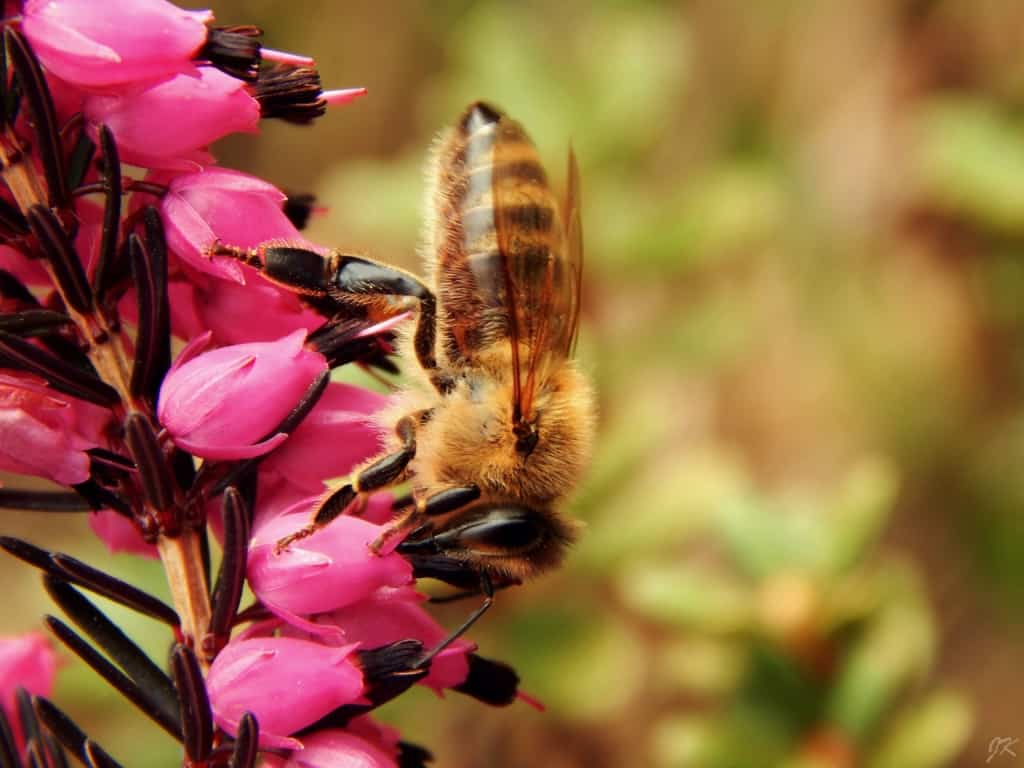

Flowers are also an essential part of the reproductive system of plants. They contain reproductive organs that produce seeds, which are necessary for the growth and survival of plants. Flowers are responsible for attracting pollinators, such as bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds, which play a critical role in the pollination process. Pollinators transfer pollen from one plant to another, allowing for cross-pollination and the production of fertilized seeds. Without pollinators, many plant species would be unable to reproduce and would eventually become extinct.
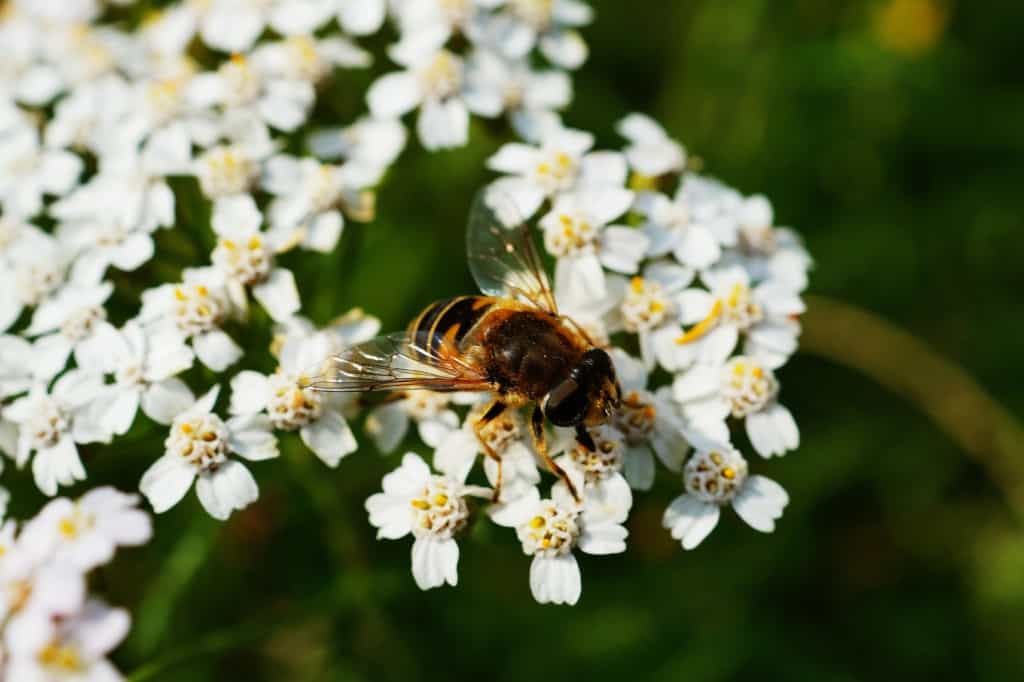

The presence of flowers and their interactions with pollinators also contribute to the maintenance of biodiversity in ecosystems. Flowers come in a variety of colours, shapes, and sizes, and their diversity helps to attract a wide range of pollinators, which in turn helps to ensure the genetic diversity of plants. Flowers and pollinators also play a role in maintaining the structure and stability of ecosystems, as they help to control the populations of herbivores, parasites, and predators.
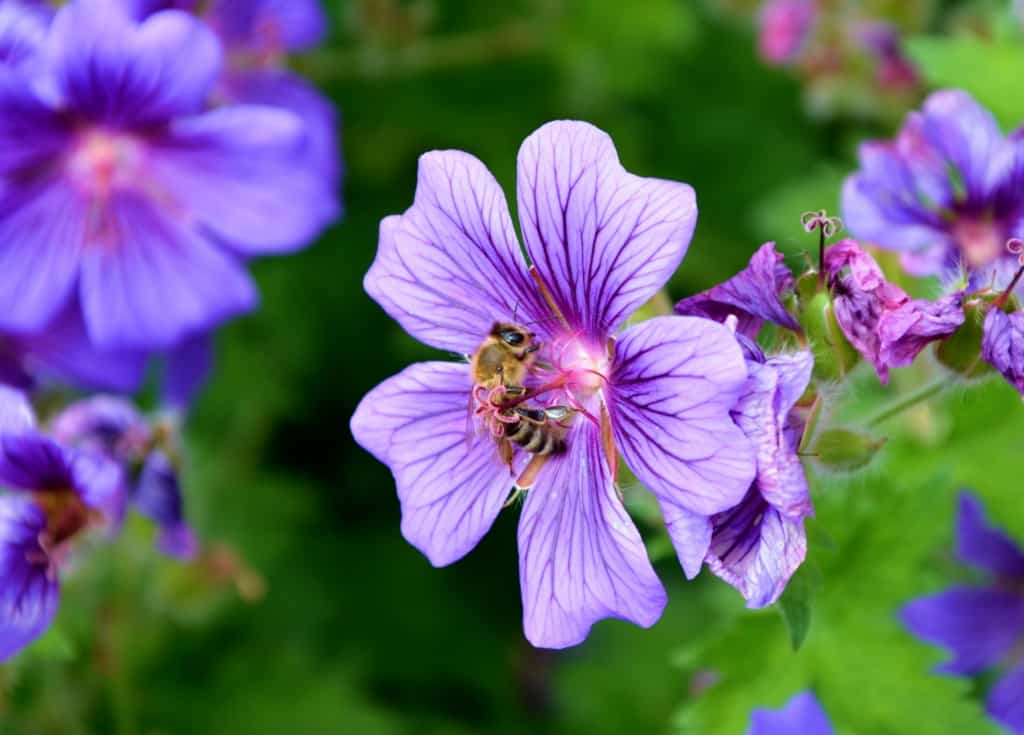

In conclusion, flowers are an essential component of the ecological system, as they provide essential resources to various organisms, including insects, birds, and small mammals. Flowers also play a critical role in the reproductive process of plants and the maintenance of biodiversity in ecosystems. Without flowers, many species of plants, insects, and birds would face extinction, which would have significant implications for the overall health and stability of ecosystems.
Management Strategies to Support Bee Populations and Enhance Pollination
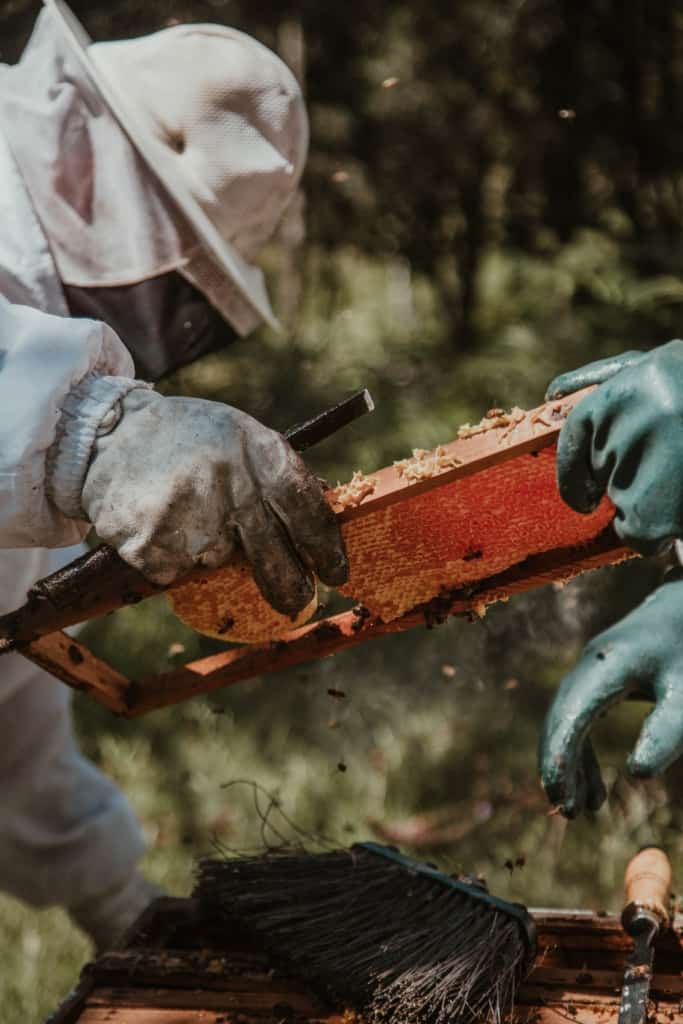

Best Management Practices for Supporting Bee Populations
Bees play a crucial role in the pollination of crops and wildflowers, and their populations have been declining in recent years due to a variety of factors, including habitat loss, pesticide use, and climate change. Effective management strategies are needed to support bee populations and ensure the continued health of ecosystems and food production. Here are some of the best management practices for supporting bee populations:
- Providing habitats for bees: Bees need a variety of habitats, including foraging areas, nesting sites, and shelter. Providing these habitats can be as simple as planting a variety of flowering plants, including native species, and maintaining un-mowed grassy areas or wildflower meadows.
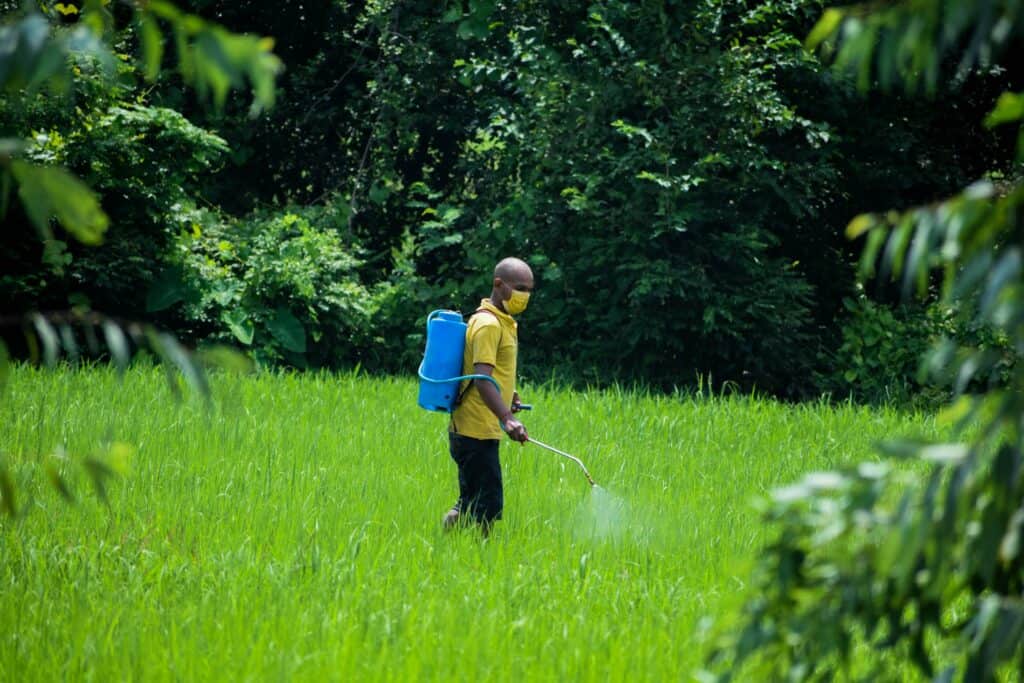
- Minimizing pesticide use: Pesticides can be harmful to bees and other pollinators, and reducing their use can help support bee populations. Farmers and gardeners can minimize pesticide use by using integrated pest management strategies, such as using pheromone traps and releasing beneficial insects, and avoiding spraying flowers when they are in bloom.
- Monitoring bee populations: Monitoring bee populations can help identify areas where management strategies are needed and track changes in bee populations over time. This can be done through citizen science programs, such as the Great Sunflower Project, or by working with local organizations, such as beekeeping clubs or university extension programs.
- Educating the public: Raising public awareness about the importance of bees and the steps that can be taken to support their populations can help create a more bee-friendly environment. This can be done through community events, school programs, and media outreach.

Strategies for Enhancing Pollination Success
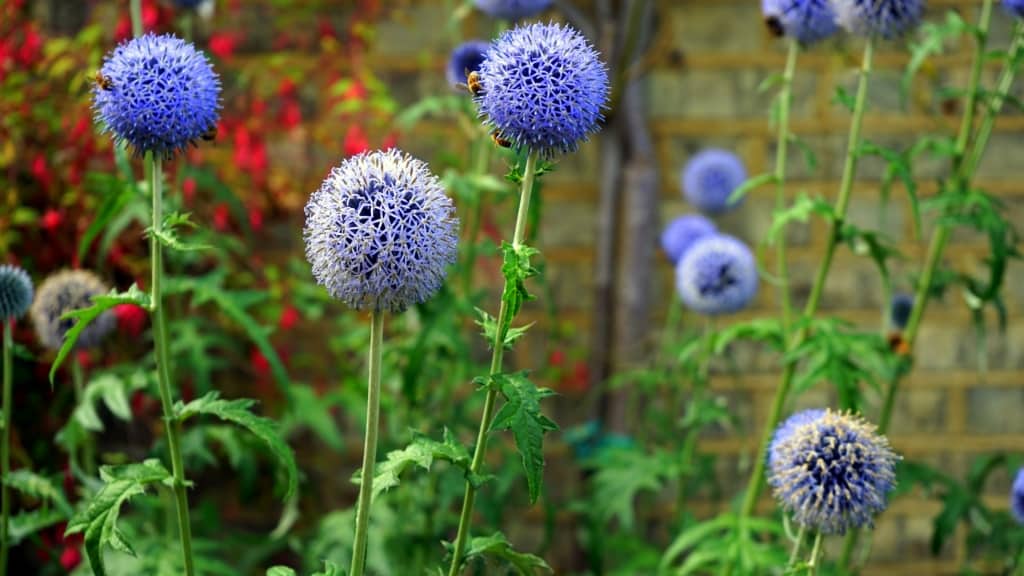

Enhancing pollination success is essential for the health of ecosystems and food production. Here are some strategies for enhancing pollination success:
- Using wildflowers: Wildflowers provide a variety of food sources for bees and other pollinators and can help support bee populations. They can be incorporated into landscapes by planting native species, such as black-eyed Susan, bee balm, and purple coneflower, or by maintaining wildflower meadows.
- Supporting bee habitats: Providing habitats for bees, such as nesting sites and shelter, can help support bee populations and enhance pollination success. This can be done by creating wildflower meadows, planting a variety of flowering plants, and maintaining un-mowed grassy areas.
- Encouraging bee-friendly farming practices: Bee-friendly farming practices, such as planting cover crops, reducing tillage, and minimizing pesticide use, can help support bee populations and enhance pollination success. Farmers can also work with beekeepers to provide habitats for bees on their farms.

The Importance of Monitoring and Protecting Bee Populations
Monitoring and protecting bee populations is essential for the future of both flowers and food production. Here are some of the reasons why it is essential:
- Ecosystem health: Bees and other pollinators play a crucial role in the pollination of crops and wildflowers, and their populations have a direct impact on the health of ecosystems. Monitoring and protecting bee populations can help ensure the continued health of ecosystems.
- Food production: Bees are responsible for pollinating more than a third of the world’s food crops, and their populations have a direct impact on food production. Monitoring and protecting bee populations can help ensure the continued production of food crops.
- Biodiversity: Bees play a crucial role in maintaining the biodiversity of ecosystems, and their populations have a direct impact on the diversity of flowering plants

The role of government and organizations in protecting and promoting bee populations
The role of the government in protecting and promoting bee populations is crucial. Governments play a critical role in implementing policies and regulations that support the preservation and protection of bee populations, as well as their habitats. Some examples of government policies and initiatives include:
- Bee protection laws: Governments have implemented various bee protection laws, such as the European Union’s ban on neonicotinoid pesticides, which have been shown to harm bee populations. This law was established to protect honeybees and other bee species from exposure to harmful chemicals.
- National Pollinator Strategy: Some countries, such as the United States, have implemented National Pollinator Strategies, aimed at promoting the health of pollinators, including bees, butterflies, and birds. This strategy includes provisions for the protection of habitats, the reduction of pesticide exposure, and the promotion of research on pollinator health.
- Agricultural subsidies: Governments also provide subsidies and incentives to farmers who implement environmentally-friendly practices, such as planting wildflowers and reducing pesticide use, which can help to support bee populations.

The role of non-government organizations in bee conservation
Non-government organizations also play a significant role in protecting and promoting bee populations. These organizations work towards the preservation and protection of bee habitats, as well as the education and awareness of the importance of bees. Some examples of non-government organizations that are dedicated to bee conservation include:
- The Xerces Society: This non-profit organization works towards the protection of invertebrates, including bees, and their habitats. They offer various programs and initiatives, including habitat restoration, advocacy, and research, aimed at promoting the health of bee populations.
- Bee-Friendly Farming: This organization works with farmers and landowners to promote the health of pollinators, including bees, through the implementation of bee-friendly practices. They provide educational resources, workshops, and certification programs to support farmers in their efforts to protect and promote bee populations.
- Friends of the Earth: This environmental advocacy group works towards promoting sustainable agriculture and reducing the use of harmful pesticides, which can harm bee populations. They also advocate for the protection of bee habitats and raise awareness about the importance of bees for food production and the environment.

Community involvement and education programs
Community involvement and education programs play an important role in protecting and promoting bee populations. These programs aim to raise awareness about the importance of bees and encourage individuals to take action in supporting bee populations. Some examples of community involvement and education programs include:
- Beekeeping classes and workshops: These classes and workshops offer individuals the opportunity to learn about beekeeping and the importance of bees for food production and the environment. They provide hands-on experience and education about the management and care of bees.
- Citizen science programs: Citizen science programs, such as the Great Sunflower Project, provide opportunities for individuals to get involved in bee research and monitoring. Participants can collect data on bee populations and contribute to our understanding of bee health and habits.
- Community gardening initiatives: Community gardening initiatives, such as community gardens and school gardens, provide opportunities for individuals to learn about the importance of pollinators and to create habitats for bees. These initiatives also promote community engagement and education about the importance of bees.

In conclusion, the protection and promotion of bee populations require the involvement of the government, non-government organizations, and individuals. Through the implementation of government policies, non-government initiatives, and community involvement and education programs, we can support and enhance the health of bee populations and the vital role they play in food production and the environment.
Types of Flowers Bees Love:
Lily – A popular ornamental plant with large, fragrant flowers in various colours, including white, yellow, orange, pink, and red.
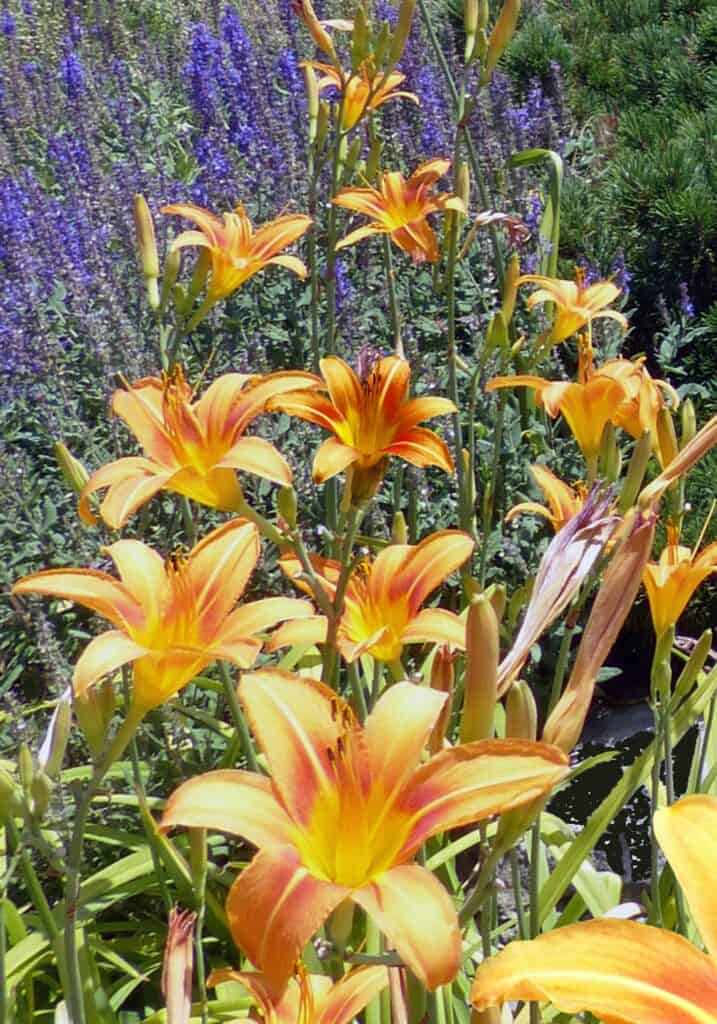

The lily is a popular flower that comes in various species and varieties, including the trumpet lily, Asiatic lily, and day lily. They are prized for their beautiful, fragrant blooms and are often used in cut flower arrangements. Lilies are typically easy to grow and are suitable for many different garden styles, from formal gardens to cottage gardens.
Sunflower – A tall and striking plant with large yellow or orange flowers that face the sun.
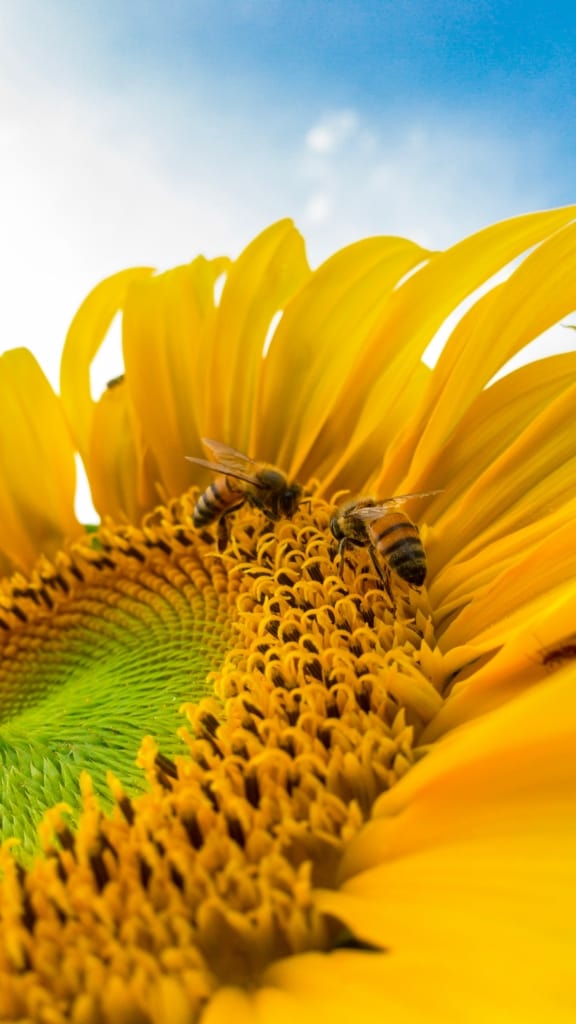

Sunflowers are known for their large, yellow blooms and cheerful appearance. They are easy to grow and are a popular choice for gardens, both for their beauty and for the seeds that they produce. Sunflowers are also used in cut flower arrangements and are popular for their bright, sunny blooms.
Chrysanthemum – A vibrant and colourful flower, commonly grown for its showy blooms in various shades of yellow, pink, purple, and white.

Chrysanthemums, also known as mums, are popular garden plants and cut flowers. They come in a variety of colours, including yellow, pink, red, and white, and are known for their long-lasting blooms. Chrysanthemums are typically easy to grow and are suitable for a wide range of garden styles, from formal gardens to cottage gardens.
Tulip – A spring-blooming flower with cup-shaped blooms in a wide range of colours.
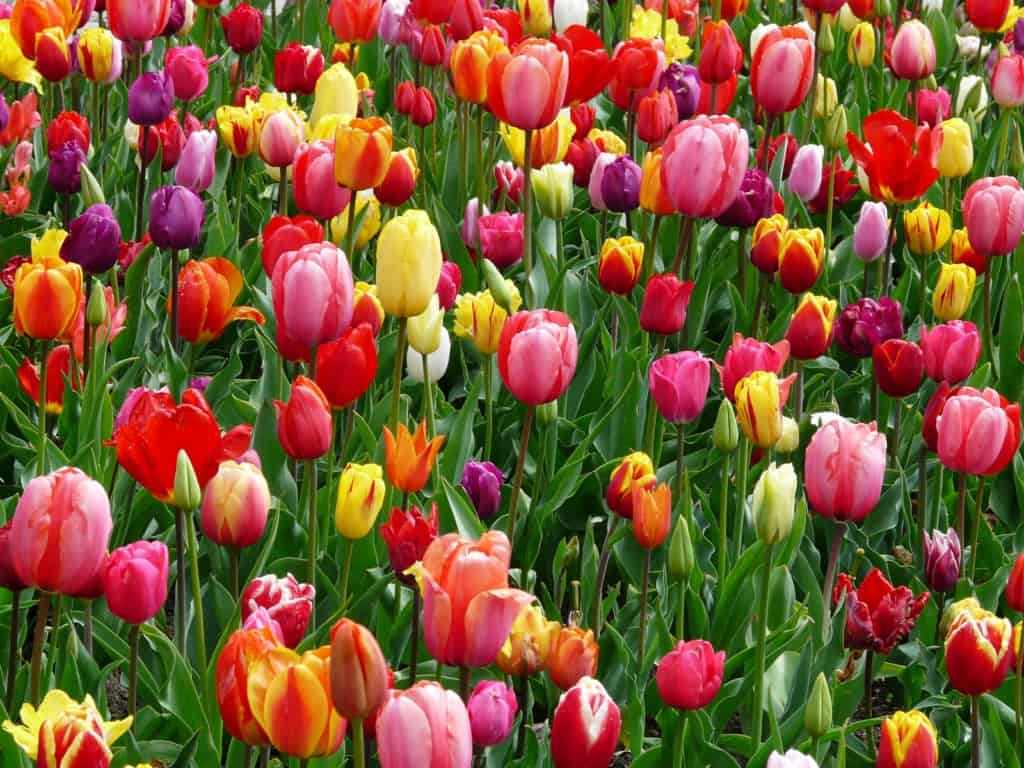

Tulips are one of the most popular spring-blooming flowers. They come in a wide range of colours and are known for their delicate blooms and sweet fragrance. Tulips are typically easy to grow and are suitable for many different garden styles, from formal gardens to cottage gardens.
Orchid – A diverse group of flowering plants, with over 25,000 species and 100,000 hybrids, known for their unique and often exotic blooms.
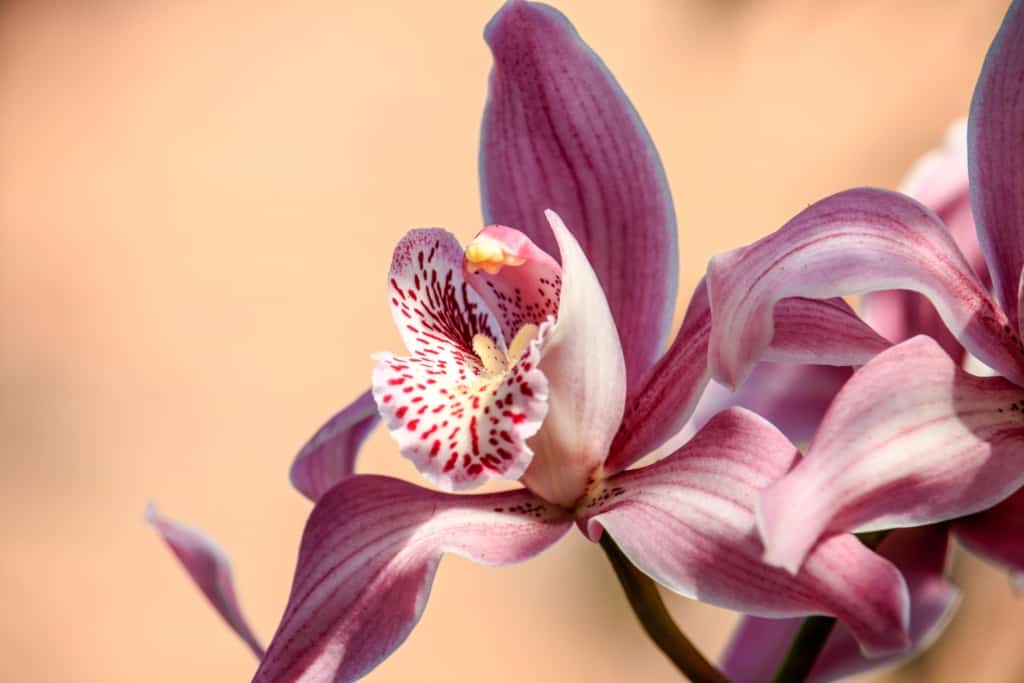

Orchids are prized for their delicate, exotic blooms and are considered one of the most beautiful flowers in the world. They come in a wide range of species and varieties and are popular as cut flowers and indoor plants. Orchids require special care but are well worth the effort for their stunning blooms.
Daisy – A wildflower with simple and classic daisy-like blooms in white and yellow.
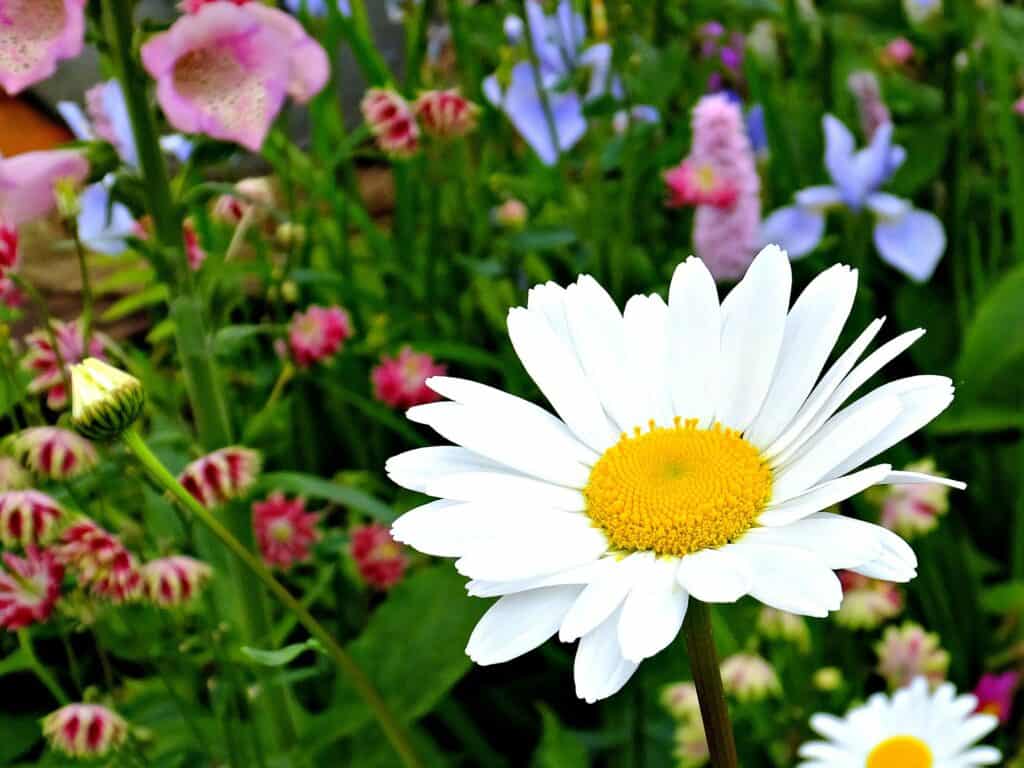

Daisies are cheerful flowers that come in many species and varieties, including the Shasta daisy and the oxeye daisy. They are known for their bright, cheerful blooms and are often used in cut flower arrangements. Daisies are typically easy to grow and are suitable for many different garden styles, from formal gardens to cottage gardens.
Marigold – A bright and cheerful flower, commonly grown for its yellow, orange, or red blooms.
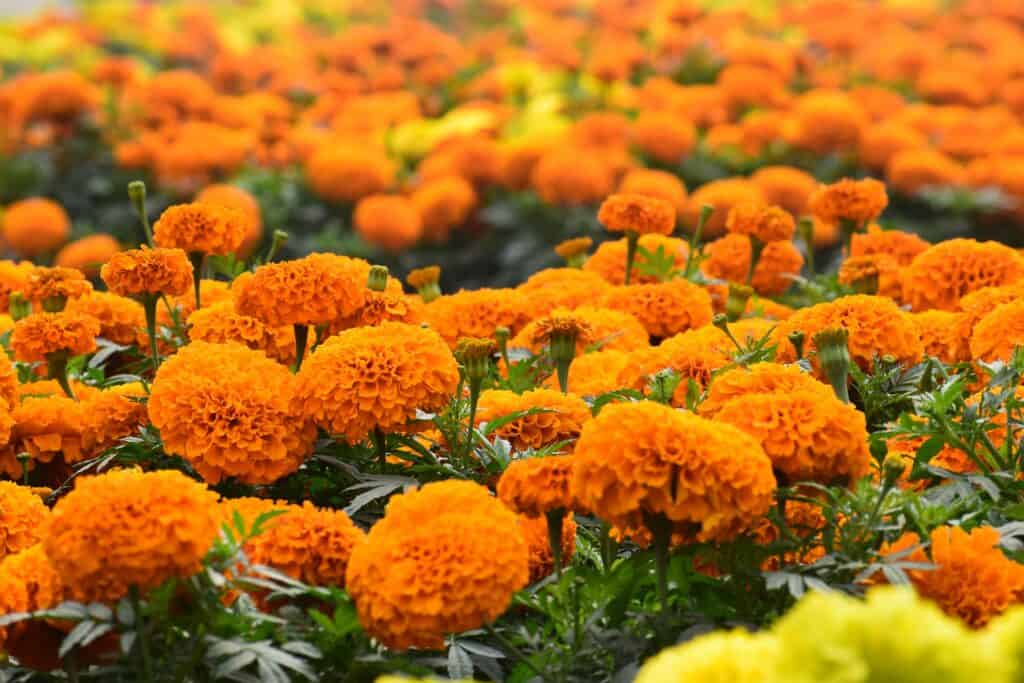

Marigolds are popular garden flowers that are known for their bright, sunny blooms. They come in many species and varieties and are easy to grow, making them a popular choice for many gardeners. Marigolds are often used in cut flower arrangements and are prized for their bright, cheerful blooms.
Carnation – A popular cut flower with fragrant, ruffled blooms in various shades of pink, red, and white.
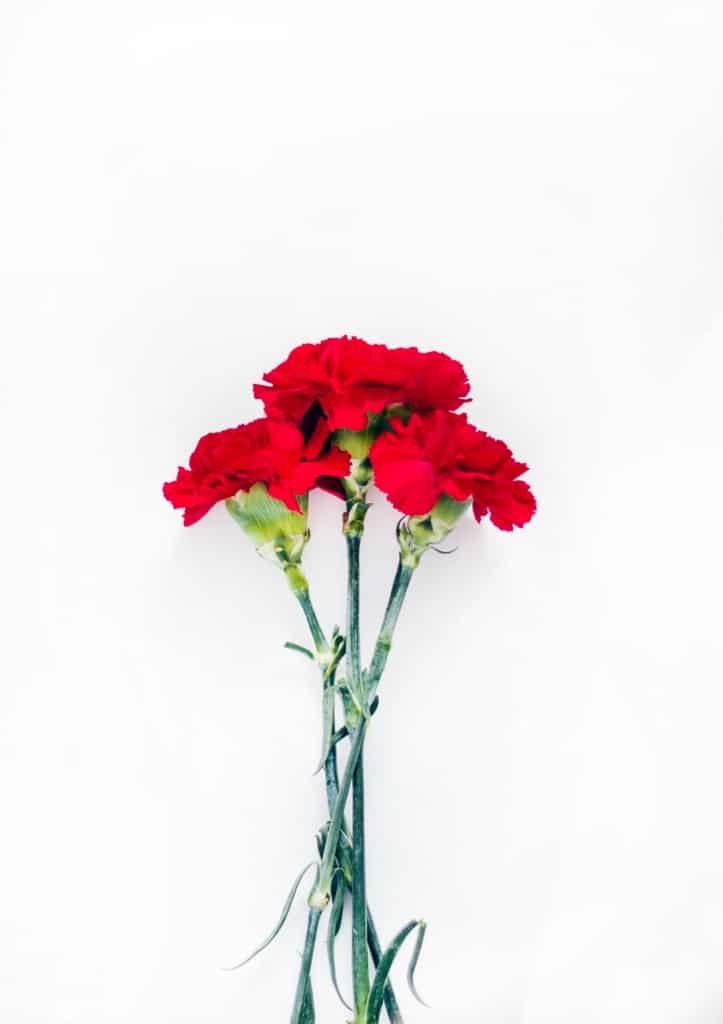

Carnations are popular cut flowers that are known for their delicate, fragrant blooms. They come in a wide range of colours, including pink, red, and white, and are prized for their long-lasting blooms. Carnations are typically easy to grow and are suitable for many different garden styles, from formal gardens to cottage gardens.
Peony – A lush and fragrant flower, with large round blooms in various colours, including pink, red, and white.
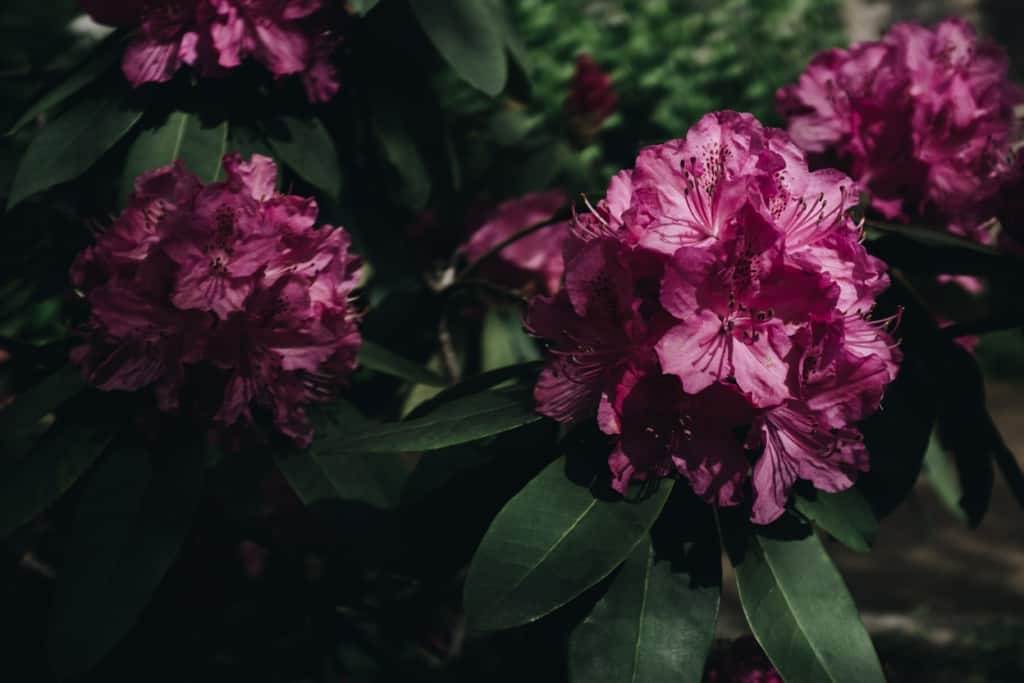

Peonies are prized for their beautiful, fragrant blooms and are considered one of the most beautiful flowers in the world. They come in a variety of species and varieties, including the tree peony and the herbaceous peony, and are popular as cut flowers and garden plants. Peonies require special care but are well worth the effort for their stunning blooms.
Hibiscus – A tropical flower with large, showy blooms in shades of red, pink, yellow, and orange.
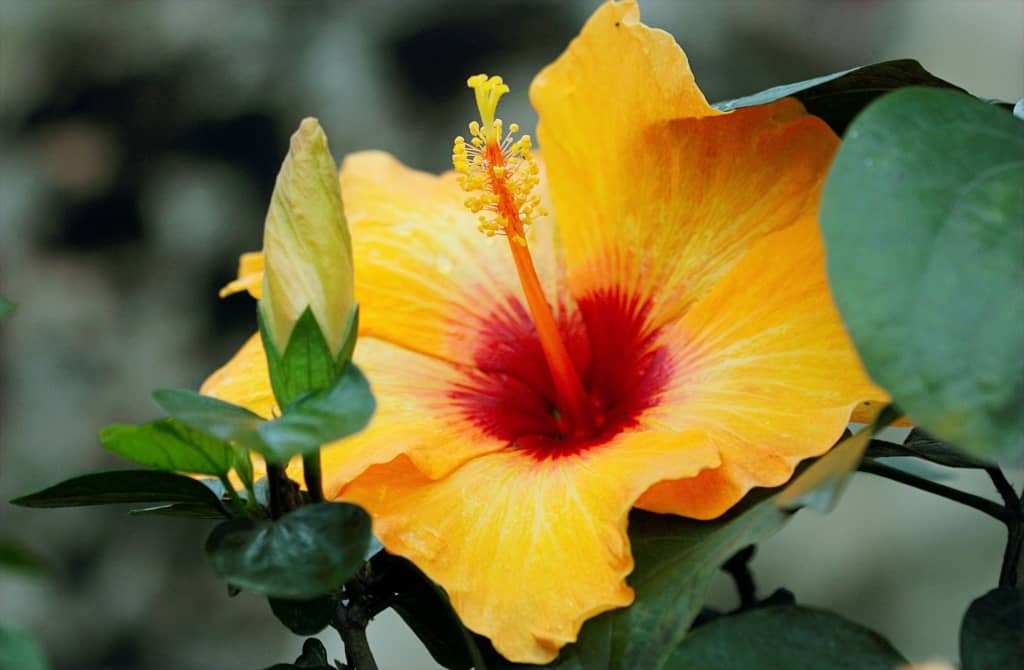

Hibiscus are exotic, tropical flowers that are known for their large, showy blooms. They come in a wide range of colours, including red, yellow, and pink, and are prized for their beauty and long-lasting blooms. Hibiscus are typically easy to grow and are suitable for many different garden styles, from formal gardens to cottage gardens.
Gerbera – A brightly coloured flower with daisy-like blooms in shades of yellow, orange, pink, and red.
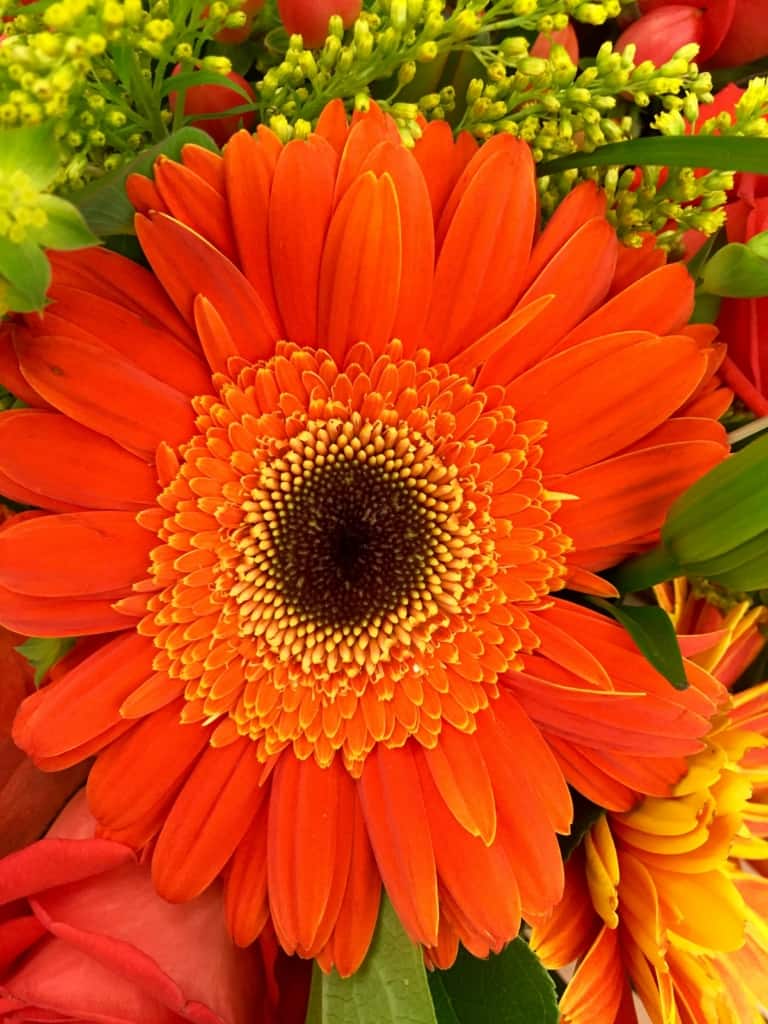

Gerbera – Gerbera is a popular ornamental flower that is known for its bright and vibrant blooms. It is part of the sunflower family and is native to South Africa. Gerberas have daisy-like blooms that can come in a variety of colours, including yellow, orange, pink, and red. The flower is also prized for its long vase life, making it a popular choice for cut flower arrangements.
Gardenia – A fragrant and attractive flower, with large, waxy blooms in white or yellow.
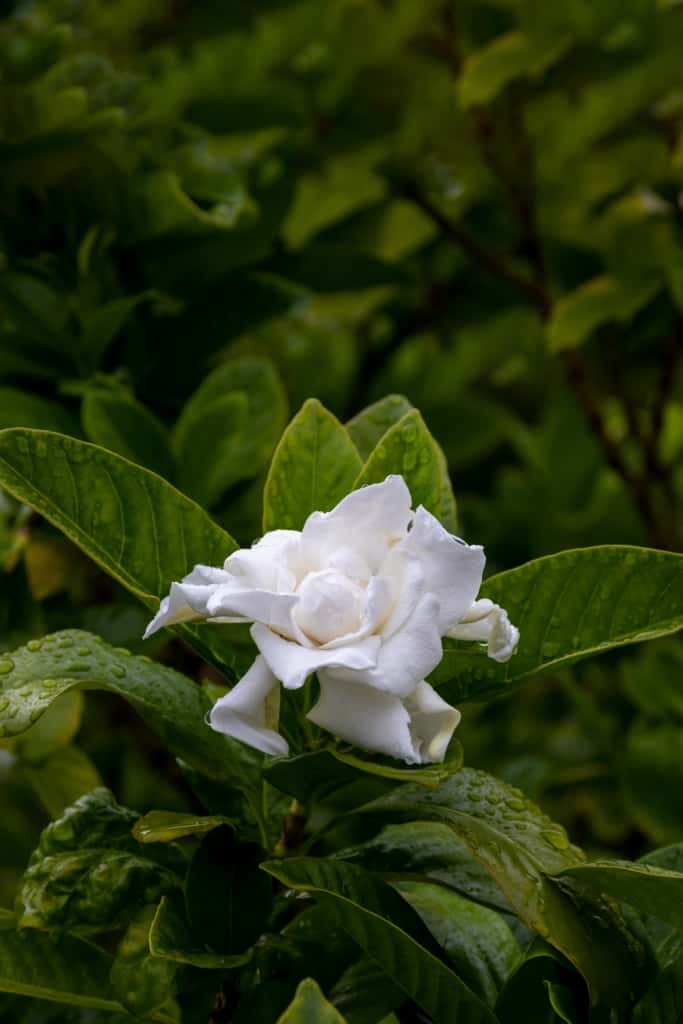

Gardenia – Gardenia is a highly fragrant and attractive flower that is often used in perfumes and perfumed products. The blooms are large and waxy and come in either white or yellow. Gardenias are native to tropical regions of Africa and Asia and are popular in temperate climates as ornamental plants. They are also used in traditional medicine to treat various ailments.
Iris – A popular garden flower, with tall spikes of blooms in a wide range of colours, including blue, purple, yellow, and white.
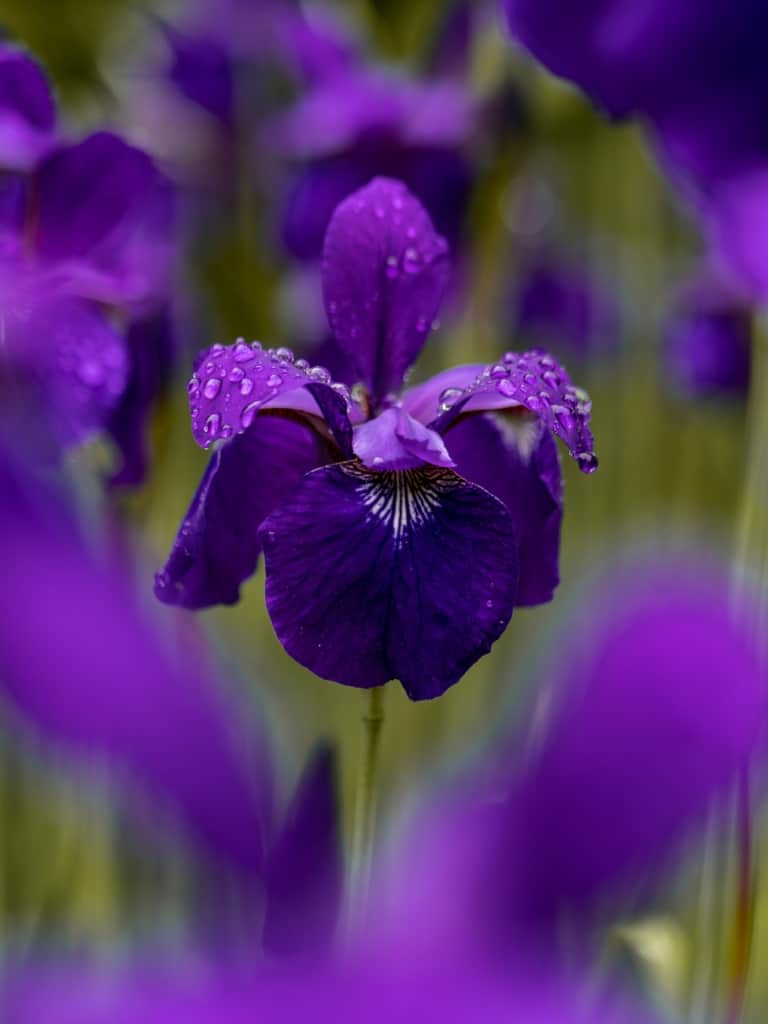

Iris – Iris is a popular garden flower that is prized for its tall spikes of colourful blooms. It is native to Europe and Asia and has been cultivated for thousands of years for its beauty and versatility. The blooms of the iris come in a wide range of colours, including blue, purple, yellow, and white. Irises are also used for their ornamental value and for their use in traditional medicine.
Freesia – A fragrant and brightly coloured flower, with tubular blooms in shades of yellow, orange, pink, red, and purple.
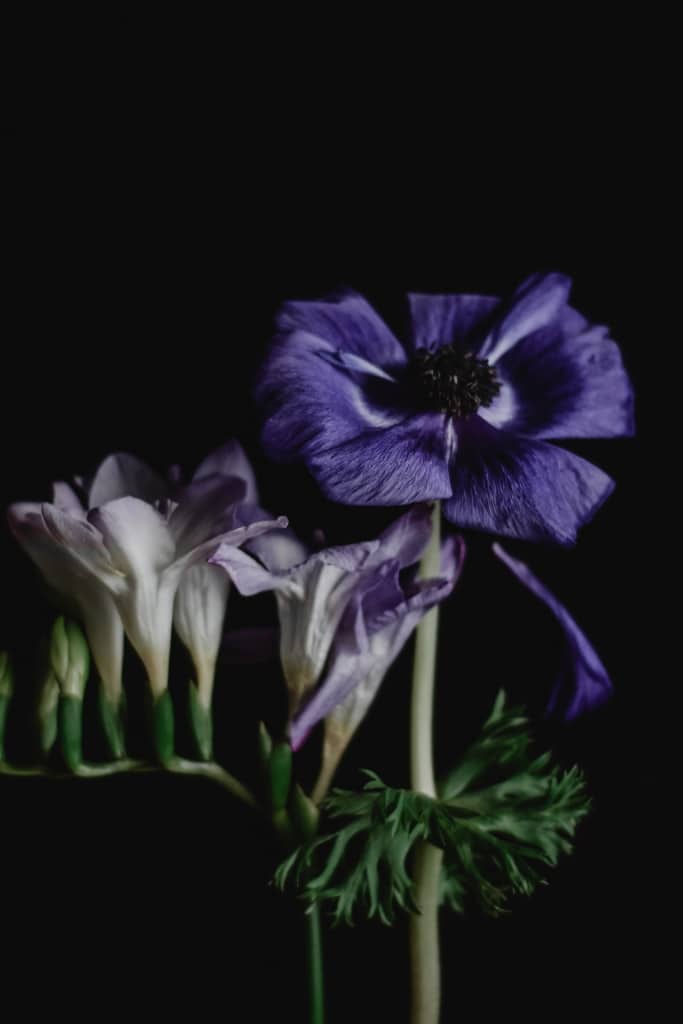

Freesia – Freesia is a fragrant and brightly coloured flower that is prized for its tubular blooms. The blooms come in a range of colours, including yellow, orange, pink, red, and purple. Freesias are native to South Africa and are popular as cut flowers, as well as for their use in perfumes and potpourri.
Hydrangea – A large, showy flower, with clusters of blooms in various shades of pink, blue, and white.
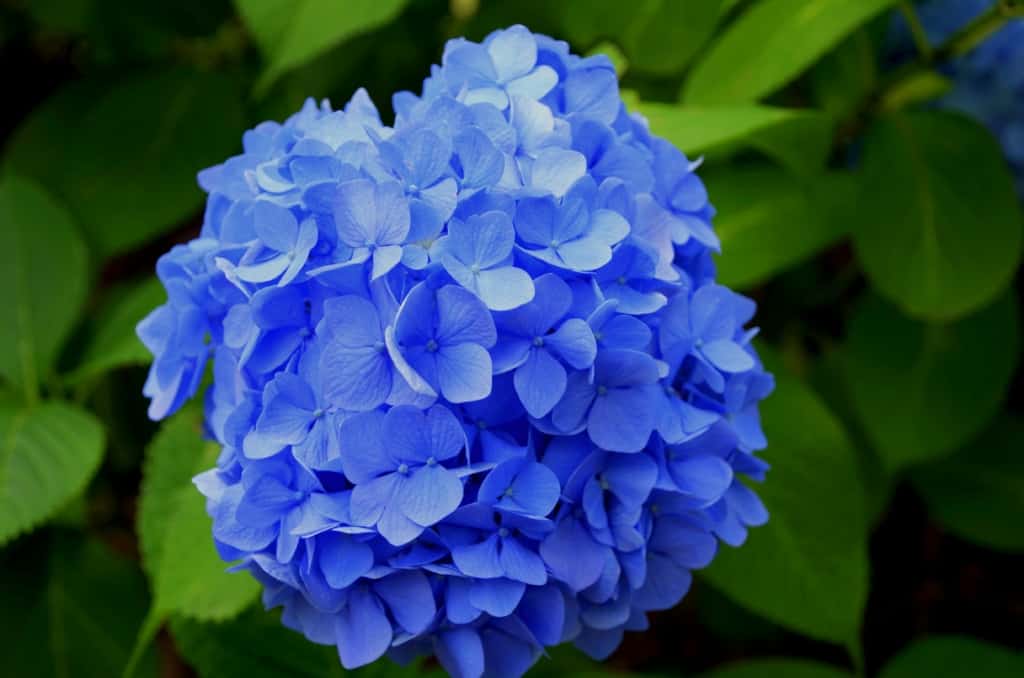

Hydrangea is a large and showy flower that is prized for its clusters of blooms. It is native to Asia and North America and is popular in temperate climates as an ornamental plant. Hydrangea blooms come in various shades of pink, blue, and white, and the flower is also used in traditional medicine.
Lily of the Valley – A delicate and fragrant flower, with small, bell-shaped blooms in white or pink.
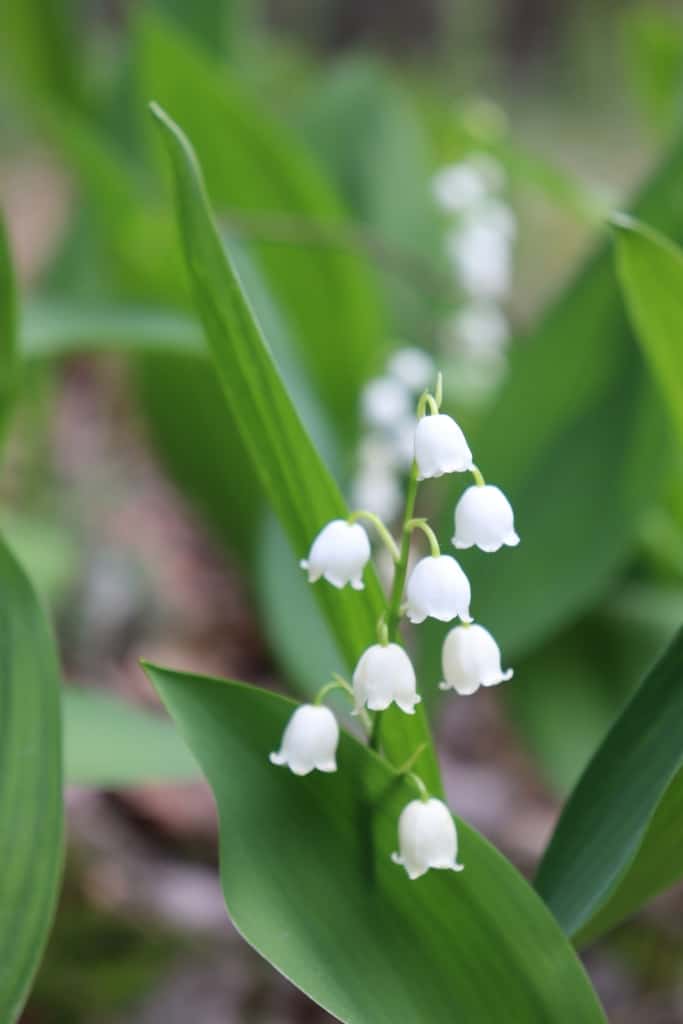

Lily of the Valley – Lily of the Valley is a delicate and fragrant flower that is prized for its small, bell-shaped blooms. The blooms come in white or pink and are often used in perfumes and potpourri. Lily of the Valley is native to Europe and Asia and is popular in temperate climates as an ornamental plant.
Gladiolus – A tall and stately flower, with spikes of large blooms in a range of colours, including red, pink, yellow, and purple.
Gladiolus is a tall and stately flower that is prized for its spikes of large blooms. It is native to South Africa and is popular in temperate climates as an ornamental plant. Gladiolus blooms come in a range of colours, including red, pink, yellow, and purple.
Pansy – A brightly coloured flower, with large, flat blooms in various colours and patterns.
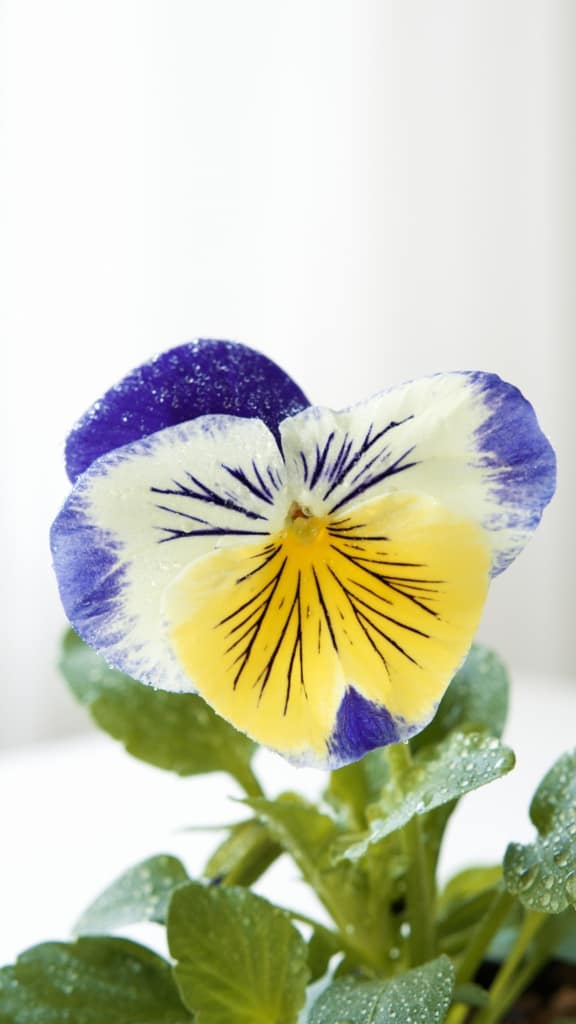

Pansy is a brightly coloured flower prized for its large, flat blooms. The blooms come in various colours and patterns and are popular as bedding plants and cut flowers. Pansies are native to Europe and Asia and are widely cultivated in temperate climates.
Sweet Pea – A fragrant and climbing plant, with delicate blooms in shades of pink, purple, red, and white.
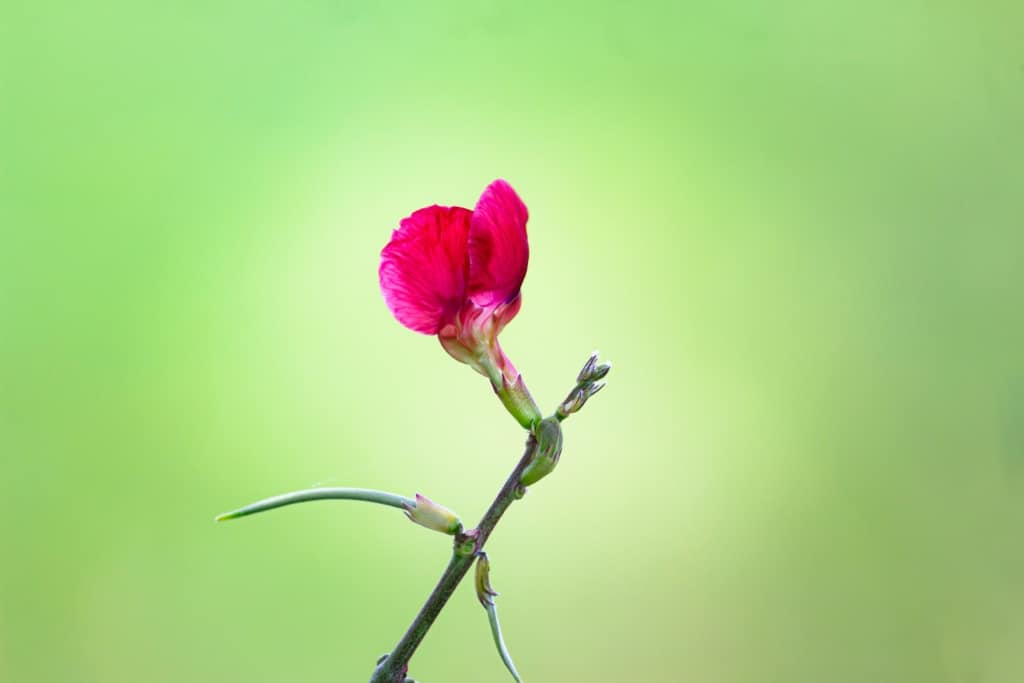

Sweet Pea is a fragrant and climbing plant that is prized for its delicate blooms. The blooms come in shades of pink, purple, red, and white, and the plant is often used in cut flower arrangements. Sweet Pea is native to Italy and is widely cultivated in temperate climates.
Zinnia – A brightly coloured flower, with large daisy-like blooms in various shades of pink, red, yellow, and orange.
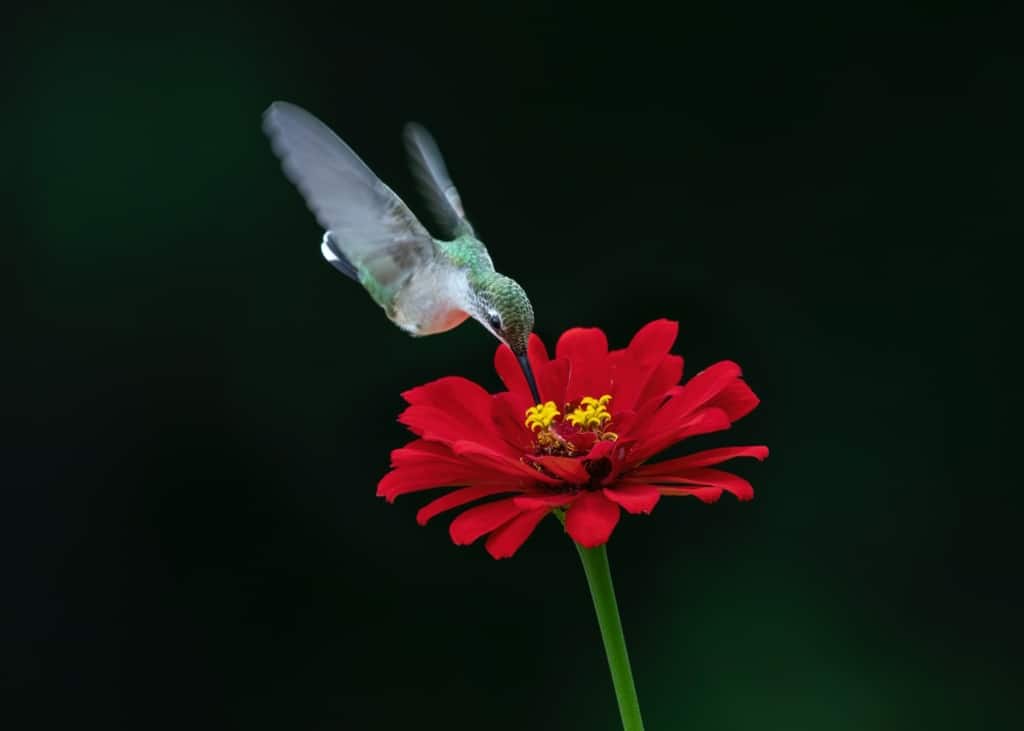

Zinnia is a brightly coloured flower that is prized for its large, daisy-like blooms. The blooms come in various shades of pink, red, yellow, and orange and are popular as bedding plants and as cut flowers. Zinnias are native to Mexico and are widely cultivated in temperate climates.
Daffodil – A popular spring-blooming flower, with large, trumpet-shaped blooms in yellow, white, and orange.
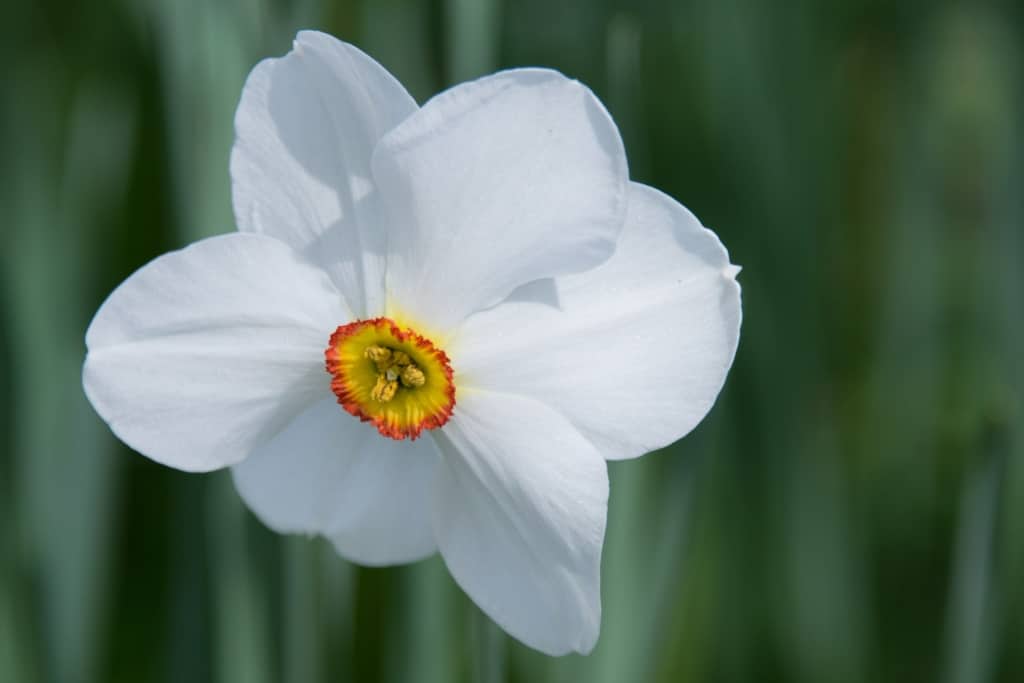

The daffodil, also known as Narcissus, is a popular spring-blooming flower native to the Mediterranean region. It’s bright yellow, white, or orange trumpet-shaped blooms are a common sight in gardens and parks and are often associated with the arrival of spring. Daffodils belong to the Amaryllidaceae family, and are easy to grow and maintain, making them a popular choice for gardeners. The daffodil is also a symbol of hope and renewal and is often used in cut flower arrangements and for naturalizing in meadows and woodland areas.
Snapdragon – A brightly coloured flower, with tall spikes of blooms in various colours, including red, pink, yellow, and orange.
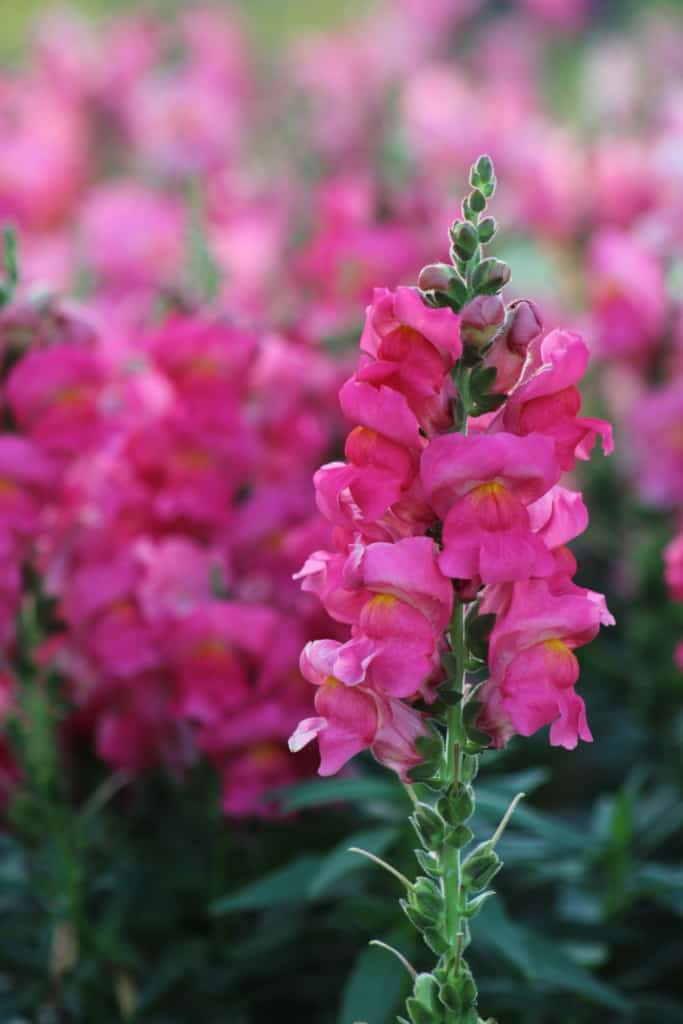

The snapdragon is a brightly coloured flower that is native to Europe and Asia. It is named for its unique blooms, which resemble the faces of dragons, with an opening and closing mouth. The snapdragon is available in a wide range of colours, including red, pink, yellow, and orange, and its tall spikes of blooms make it a popular choice for borders and cut flower arrangements. The snapdragon is a hardy and easy-to-grow plant and is often grown annually, although it can be overwintered in warmer climates.
Poppy – A brightly coloured flower, with large, papery blooms in shades of red, pink, orange, and yellow.
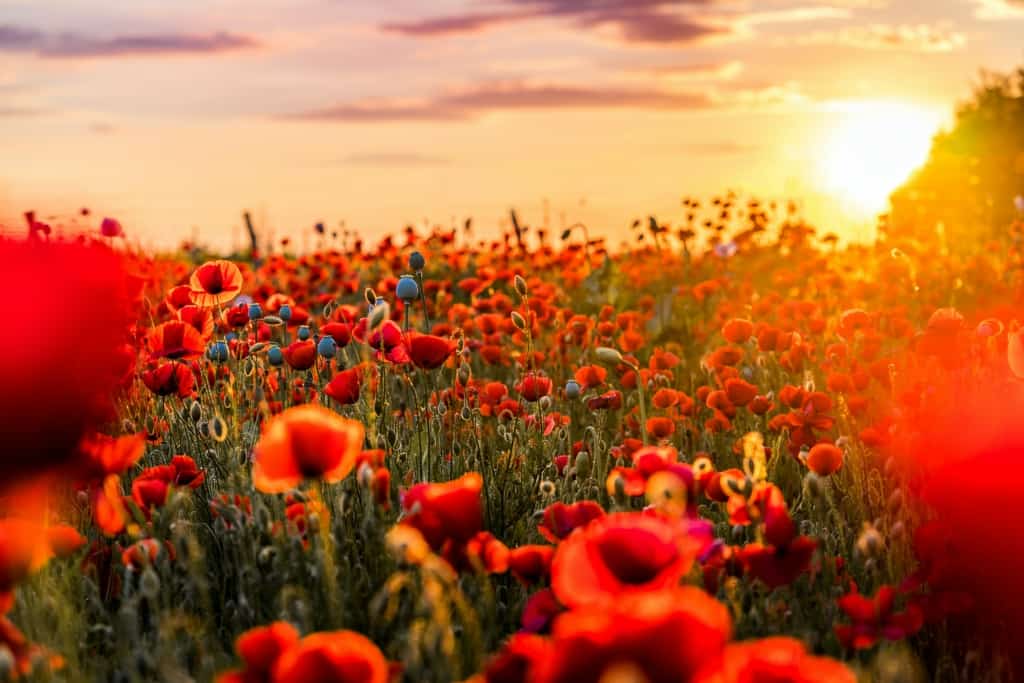

The poppy is a brightly coloured flower that is native to Europe, Asia, and North America. Its large, papery blooms come in shades of red, pink, orange, and yellow, and are often associated with the commemoration of fallen soldiers, as well as with the vibrant landscapes of fields and meadows. Poppies belong to the Papaveraceae family, and are easy to grow, making them a popular choice for gardens and meadows. They are also an important source of food for pollinators, including bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds.
Cosmo – A brightly coloured flower, with large, daisy-like blooms in shades of pink, purple, red, and white.

The cosmo, also known as the cosmos, is a brightly coloured flower that is native to Mexico and Central America. It has large, daisy-like blooms in shades of pink, purple, red, and white, and its airy, fern-like foliage makes it a popular choice for adding texture and movement to gardens and flower arrangements. The cosmo is easy to grow and maintain and is often grown annually, although it can be overwintered in warmer climates. It is also an important source of food for pollinators, including bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds, and is often used in landscaping and gardening projects to support these species.
References:
- West-Eberhard, Mary Jane. “Flowering Plants: Origin, Adaptation, and Ecological Consequences.” Ecology, vol. 87, no. 7, 2006, pp. 1345–1355., doi:10.1890/0012-9658(2006)87[1345:FPOAAC]2.0.CO;2.
- Fonseca, A. M., & Freitas, L. M. (2012). The importance of flowers in the preservation of biodiversity. Biodiversity and Conservation, 21(5), 1367-1393.
- Thompson, H. V., & Brown, M. J. F. (2009). The role of flowers and pollination in the evolution and ecology of angiosperms. Plant, Cell & Environment, 32(6), 669-683.
- Hartmann, H. T., Kester, D. E., Davies, J. E., & Geneve, R. L. (2015). Plant Propagation: Principles and Practices. Pearson.
- Kremen, C., Williams, N. M., Andermann, A., Barry, K., Cutler, A., Forero-Montaña, J., … & Klein, A. M. (2010). The value of long-term monitoring of pollinators. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 25(7), 671-675.
- Buchmann, S. L. (1987). The significance of floral characteristics in relation to honey bee foraging: A review. Apidologie, 18(3), 183-204.
- Buchmann, S. L., & Nabhan, G. P. (1996). The Forgotten Pollinators. Island Press.
- Kearns, C. A., & Inouye, D. W. (1993). Techniques for pollination biologists. University Press of Colorado.
- Ollerton, J., Winfree, R., & Tarrant, S. (2011). How many flowering plants are pollinated by animals? Oikos, 120(3), 321-326.
- West-Eberhard, Mary Jane. “Flowering Plants: Origin, Adaptation, and Ecological Consequences.” Ecology, vol. 87, no. 7, 2006, pp. 1345–1355., doi:10.1890/0012-9658(2006)87[1345:FPOAAC]2.0.CO;2.
- Fonseca, A. M., & Freitas, L. M. (2012). The importance of flowers in the preservation of biodiversity. Biodiversity and Conservation, 21(5), 1367-1393.
- Thompson, H. V., & Brown, M. J. F. (2009). The role of flowers and pollination in the evolution and ecology of angiosperms. Plant, Cell & Environment, 32(6), 669-683.
- Hartmann, H. T., Kester, D. E., Davies, J. E., & Geneve, R. L. (2015). Plant Propagation: Principles and Practices. Pearson.
- Kremen, C., Williams, N. M., Andermann, A., Barry, K., Cutler, A., Forero-Montaña, J., … & Klein, A. M. (2010). The value of long-term monitoring of pollinators. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 25(7), 671-675.
- Biesmeijer, J.C., Roberts, S.P.M., Reemer, M., Ohlemuller, R., Edwards, M., Peeters, T., Schaffers, A.P., Potts, S.G., Kleukers, R., Thomas, C.D., et al. (2006). Parallel declines in pollinators and insect-pollinated plants in Britain and the Netherlands. Science 313, 351–354.
- Garibaldi, L.A., Steffan-Dewenter, I., Kremen, C., Jesse, L.H., and Bommarco, R. (2013). Wild pollinators enhance fruit sets of crops regardless of honey bee abundance. Science 339, 1608–1611.
- National Research Council (U.S.) (2007). Status of Pollinators in North America. National Academies Press, Washington, DC.
- Oldroyd, B.P. (2007). What’s Keeping the Apis cerana out of the Hive? Animal Behaviour 74, 963–970.
- Vanbergen, A.J., and Iserbyt, A. (2011). Threats to an ecosystem service: pressures on pollinators. Front Ecol Environ 9, 5–13.
- Wilson, E.O. (1984). Biophilia. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA.
- Xie, J., and Kremen, C. (2017). Diverse and abundant bee fauna enhances crop yield in a tropical agroforest. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114, 13277–13282.
- USDA (2020). USDA Announces Investment to Support Honey Bee Health, Pollination and Production. Available at: https://www.usda.gov/newsroom/press-releases/2020/01/31/usda-announces-investment-support-honey-bee-health-pollination.
- Pollinator Partnership (2021). Pollinator-Friendly Farming. Available at: https://pollinator.org/pollinator-friendly-farming.
- The Xerces Society (2021). The Benefits of Bee Habitat. Available at: https://xerces.org/bee-habitat.